Question: 12. Let A = {A,, : ne Z, where A, = (n- 1,n+ 1). (a) Find A and prove your conjecture. (b) Find R-UA
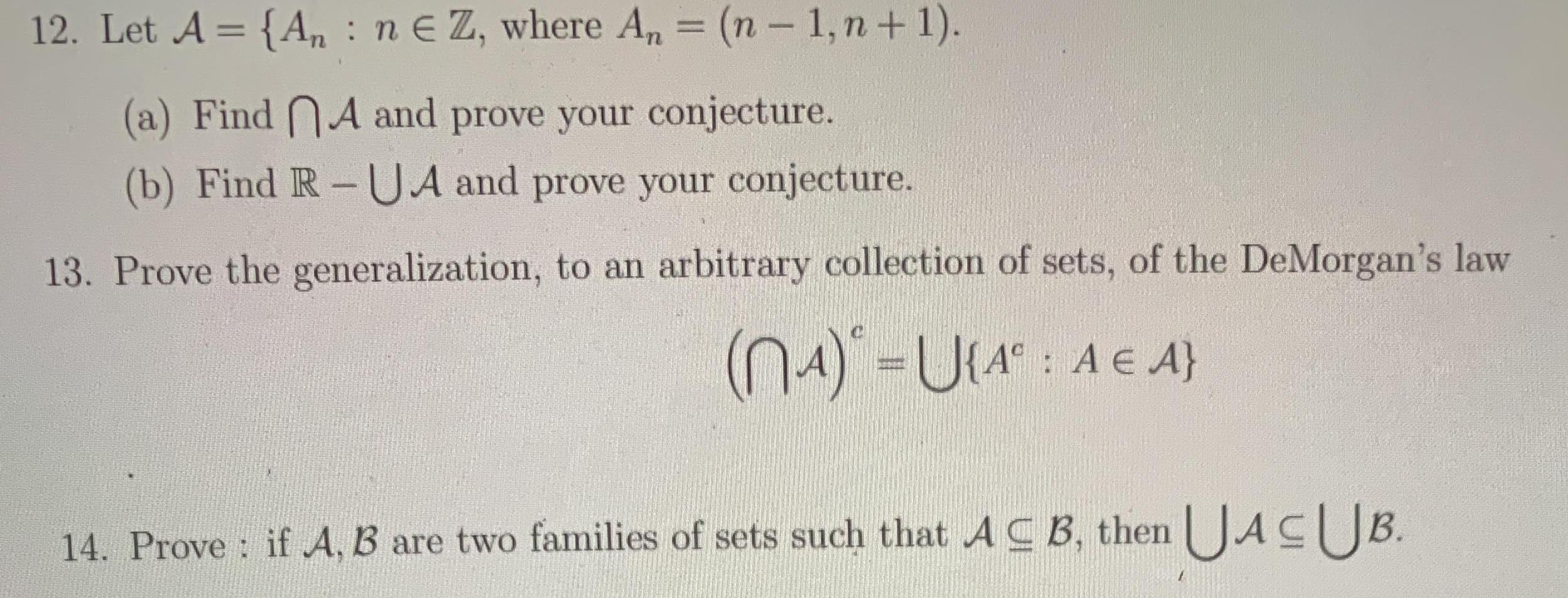
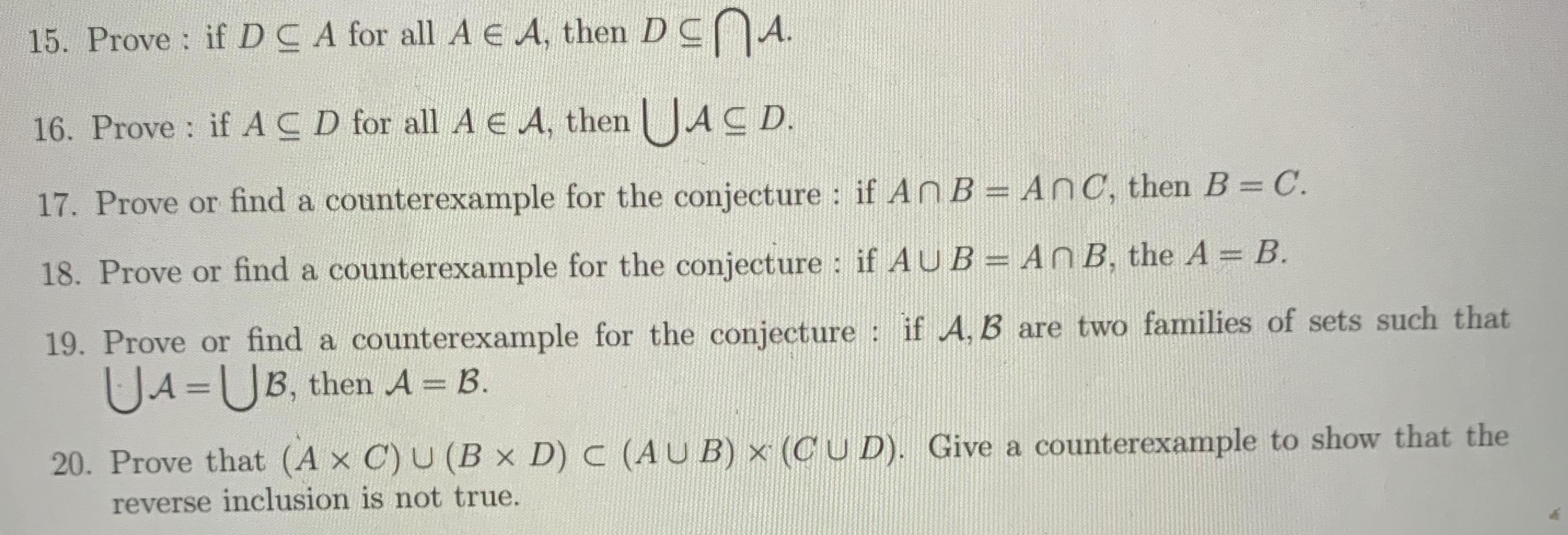
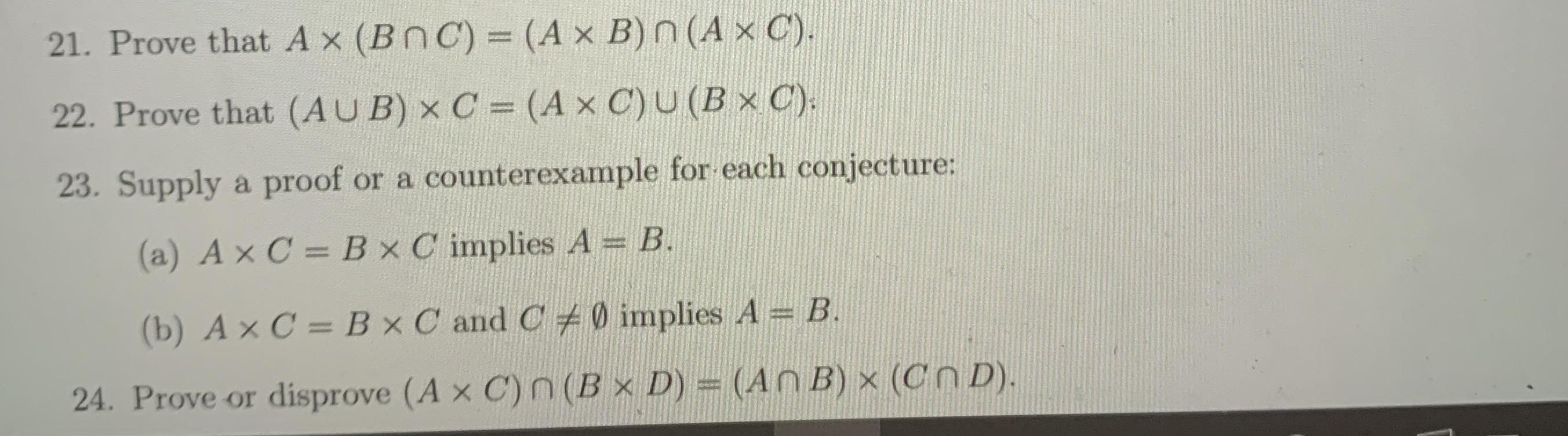
12. Let A = {A,, : ne Z, where A, = (n- 1,n+ 1). (a) Find A and prove your conjecture. (b) Find R-UA and prove your conjecture. 13. Prove the generalization, to an arbitrary collection of sets, of the DeMorgan's law 14. Prove : if A, B are two families of sets such that AC B, then JAC JB. 15. Prove : if DCA for all A E A, then DC A. 16. Prove : if A CD for all A E A, then JAC D. 17. Prove or find a counterexample for the conjecture : if An B = AnC, then B = C. %3D 18. Prove or find a counterexample for the conjecture : if AU B = An B, the A = B. 19. Prove or find a counterexample for the conjecture : if A, B are two families of sets such that UA =UB, then A = B. 20. Prove that (A x C) U (B x D) C (AU B) x (CU D). Give a counterexample to show that the reverse inclusion is not true. 21. Prove that A x (BnC) = (A B) n (A C). 22. Prove that (AUB) x C = (A x C)U(B C). %3D 23. Supply a proof or a counterexample for each conjecture: (a) Ax C = Bx C implies A = B. %3D (b) Ax C = Bx C and C #0 implies A = B. 24. Prove or disprove (A x C) n (B D) = (ANB) (Cn D).
Step by Step Solution
3.66 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


