Question: 14. first part Find the arc length parameter along the curve from the point where t=0 by evaluating the integral s = Ividt. Then find


14. first part
![. . . The arc length parameter is s(t) =]. (Type an](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6679a62de6930_4296679a62dd3d50.jpg)

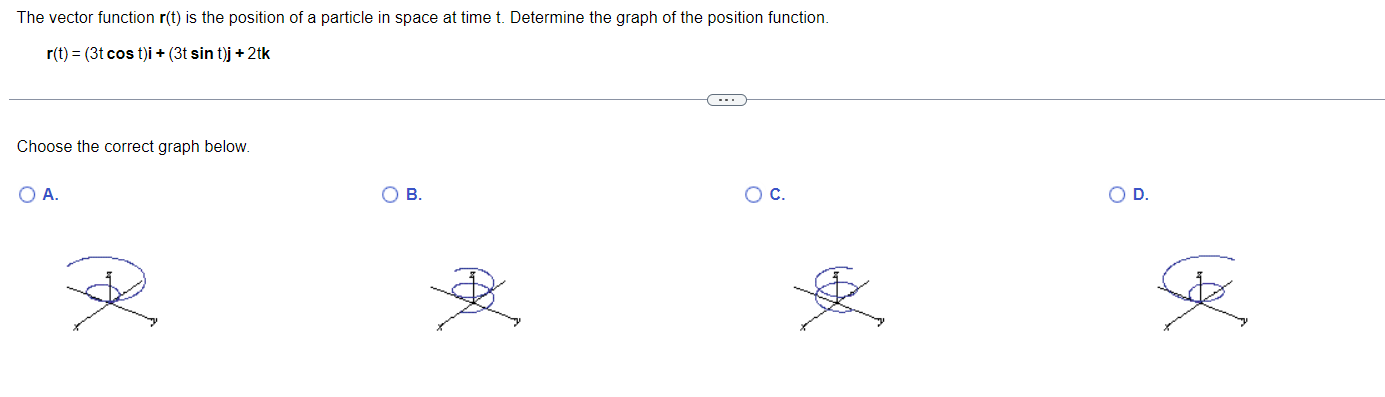
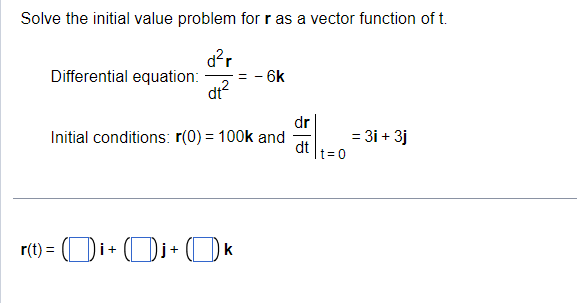


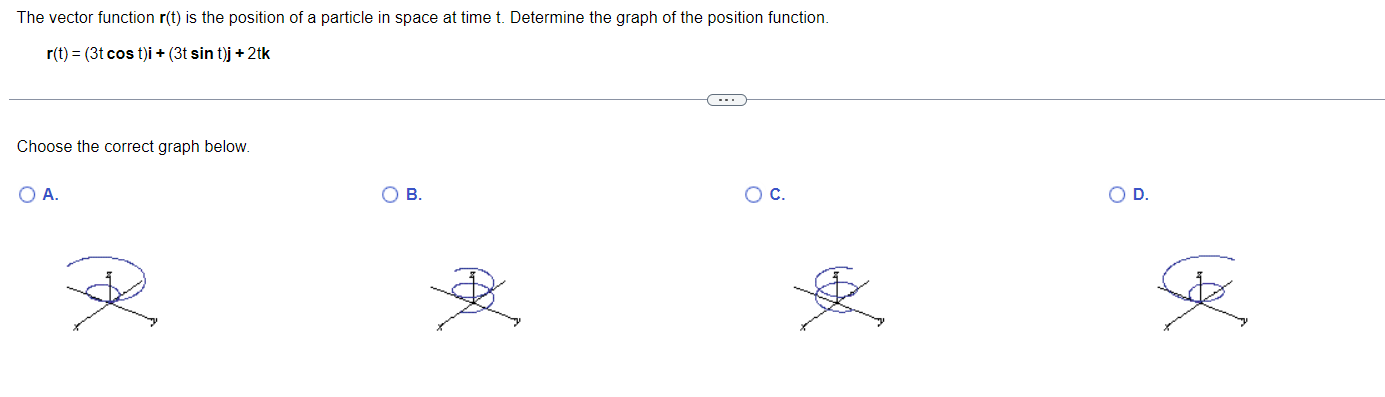
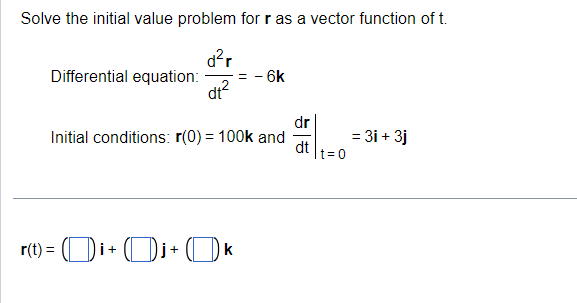
Find the arc length parameter along the curve from the point where t=0 by evaluating the integral s = Ividt. Then find the length of the indicated portion of the curve. 0 r(t) = (5e cost) i+ (5e sint) j - 5elk, - In4sts0 . . . The arc length parameter is s(t) =]. (Type an exact answer, using radicals as needed.)To illustrate that the length of a smooth space curve does not depend on the parameterization used to compute it, calculate the length of one turn of the helix with the following parameterizations. a. r(t) = (cos 4t)i + (sin 4t)j + 4tk, Ost= b. r(t) = cos 1= 2W c. r(t) = (cost)i - (sin t)j - tk, - 2nsts0 Note that the helix shown to the right is just one example of such a helix, and does not exactly correspond to the parametrizations in parts a, b, or c. (1, 0,0) =0 . . . a. L = (Type an exact answer, using it as needed.)The vector function r(t) is the position of a particle in space at time t. Determine the graph of the position function. r(t) = (3t cos t)i + (3t sin t)j + 2tk . . . Choose the correct graph below. O A. O B. O C. O D.Solve the initial value problem for r as a vector function of t. Differential equation: - 6k dr Initial conditions: r(0) = 100k and = 3i + 3j dt 1= 0 r(t ) = kI Find the arc length parameter along the given curve from the paint where t = O by evaluating the integral 5(t) = J|v('c)| d": Then find the length ofthe indicated portion of the curve rtt) = 8cost i + 85int 0 j+81KwhereOsts bl: The arc length parameter along the curve starting at t: 0 is 5(t) : (Type an exact answer, usrng radicals as needed.) The path r(t) = (3 cos t) i + (3 sin t) j describes motion on the circle x + y =9. Find the particle's velocity and acceleration vectors at t= - and , and sketch them as vectors on the curve. . . . The velocity vector at t = g is v * = (ID.+ (Di (Type exact answers, using radicals as needed.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


