Question: 17. (a) (b) (C) (d) (e) (1) (g) In a study of memory recall, 5 people were given 10 minutes to memorize a list of
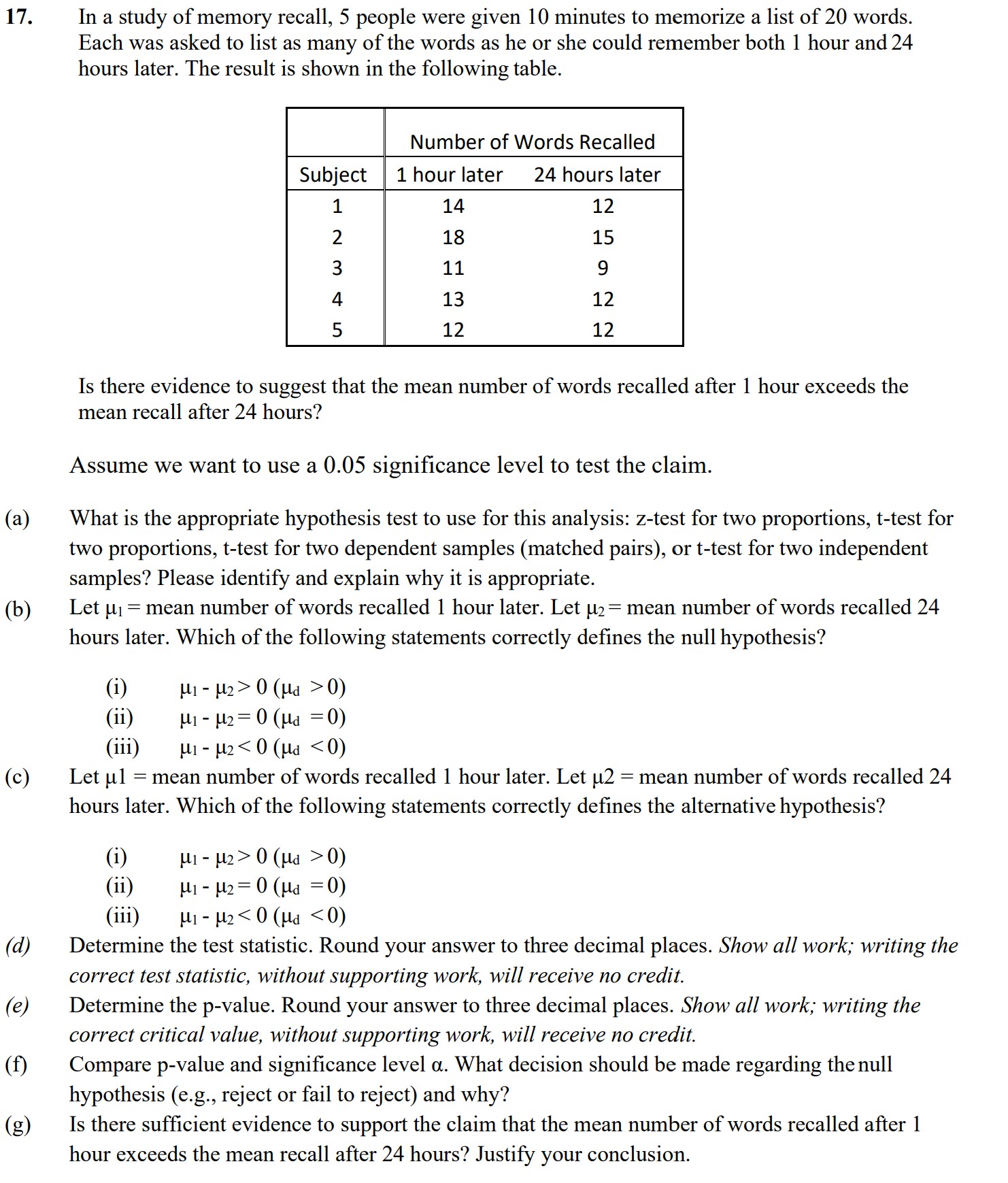
17. (a) (b) (C) (d) (e) (1) (g) In a study of memory recall, 5 people were given 10 minutes to memorize a list of 20 words. Each was asked to list as many of the words as he or she could remember both 1 hour and 24 hours later. The result is shown in the following table. - Number of Words Recalled Subject 1 hour later 24 hours later Is there evidence to suggest that the mean number of words recalled after 1 hour exceeds the mean recall after 24 hours? Assume we want to use a 0.05 signicance level to test the claim. What is the appropriate hypothesis test to use for this analysis: Z-test for two proportions, ttest for two proportions, t-test for two dependent samples (matched pairs), or t-test for two independent samples? Please identify and explain why it is appropriate. Let 111 = mean number of words recalled 1 hour later. Let u; = mean number of words recalled 24 hours later. Which of the following statements correctly denes the null hypothesis? (i) ul-u2>0(ud >0) (ii) rm - FF 0 (Ha =0) (iii) ill - P2 0(ud >0) (ii) m- 112:0(r1d =0) (iii) [11' u2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


