Question: 18181 Question 39 (1 point) Relative purchasing parity is defined as 1) domestic inflation minus foreign inflation (ES/Et-ES/Et-1/ES/CI-1. 2) foreigs inflation minus domestic inflation-S/C-ES/C1-1/ES/C+-1 3)
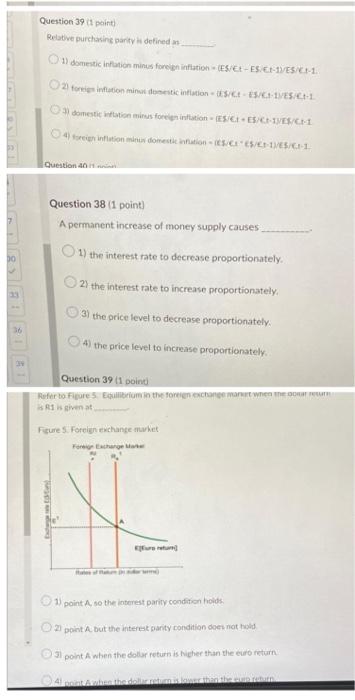
18181 Question 39 (1 point) Relative purchasing parity is defined as 1) domestic inflation minus foreign inflation (ES/Et-ES/Et-1/ES/CI-1. 2) foreigs inflation minus domestic inflation-S/C-ES/C1-1/ES/C+-1 3) domestic inflation minus foreign inflation (ES/CI-ES/C-13/ES/CH 4) foreigh inflation minus domestic inflation (ES/CI ES/C-1)/ES/C-1 Question 40 Question 38 (1 point) A permanent increase of money supply causes, 1) the interest rate to decrease proportionately. 2) the interest rate to increase proportionately. 3) the price level to decrease proportionately. 4) the price level to increase proportionately. Question 39 (1 point) Refer to Figure 5. Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market when the cour return is R1 is given at Figure 5. Foreign exchange market Foreign Exchange Marke Eur 1) point A, so the interest parity condition holds 2) point A, but the interest parity condition does not hold 31 point A when the dollar return is higher than the euro return
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


