Question: 1g). Be sure to answer all questions here: Let's say that you are concerned that the intravenous saline solution that people receive upon admission to
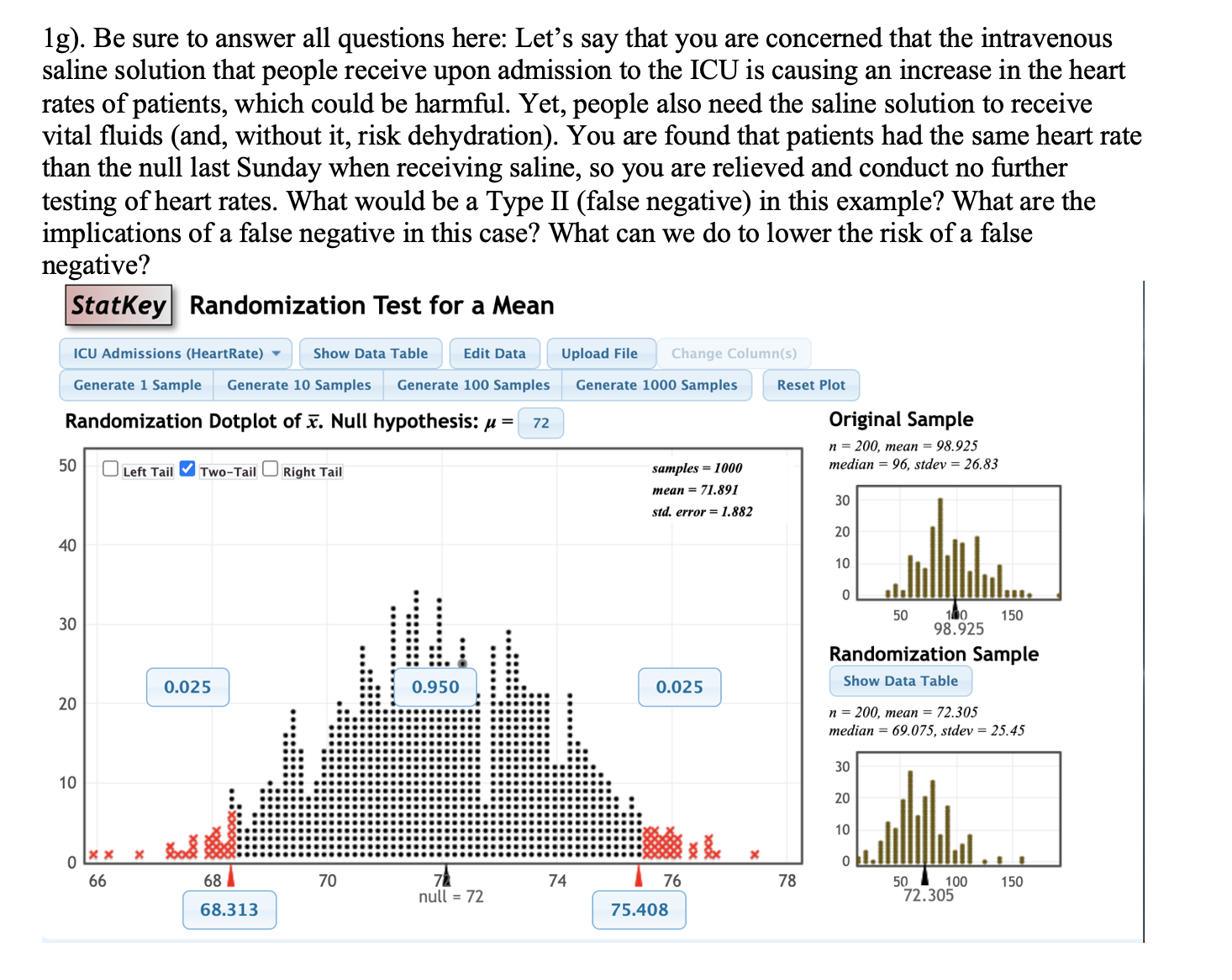
1g). Be sure to answer all questions here: Let's say that you are concerned that the intravenous saline solution that people receive upon admission to the ICU is causing an increase in the heart rates of patients, which could be harmful. Yet, people also need the saline solution to receive vital uids (and, without it, risk dehydration). You are found that patients had the same heart rate than the null last Sunday when receiving saline, so you are relieved and conduct no further testing of heart rates. What would be a Type II (false negative) in this example? What are the implications of a false negative in this case? What can we do to lower the risk of a false negative? Randomization Test for a Mean ICU Admissions (Heartkate) v Generate 1 Sample Randomization Dotplot of 1?. Hull hypothesis: p = U Left Tall Two-Tall Cl nght Tall Show Data Table Generate 10 Samples - Edit Data Upload File Generate 100 Samples Ina-nonuouoe- null = 72 72' Generate 1000 Samples mean = 71.59! std. emr = 1.382 Ci'rntq-Q CLIIL " 'i' Reset Plot Original Sample n = 200, mean = 98.925 median : 96. sfd'ev : 26.83 30 20 1D 0 50 150 1 93.925 Randomization Sample Show Data Table I! = 200, mean = 72.305 median = 69.075, stdev = 25.45 30 20 10 50 100 150 72.305
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


