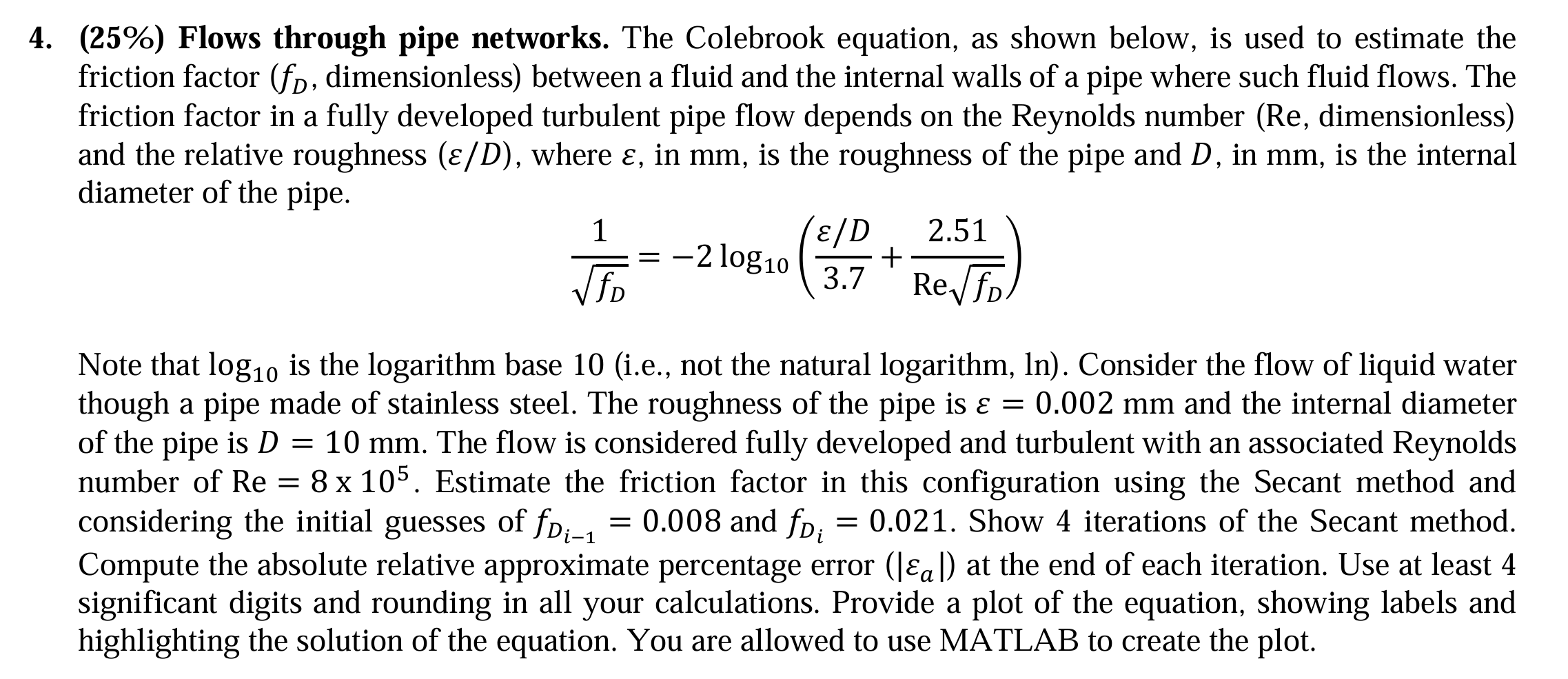
Question: ( 2 5 % ) Flows through pipe networks. The Colebrook equation, as shown below, is used to estimate the friction factor ( f D
Flows through pipe networks. The Colebrook equation, as shown below, is used to estimate the
friction factor dimensionless between a fluid and the internal walls of a pipe where such fluid flows. The
friction factor in a fully developed turbulent pipe flow depends on the Reynolds number Re dimensionless
and the relative roughness where in mm is the roughness of the pipe and in mm is the internal
diameter of the pipe.
Note that is the logarithm base ie not the natural logarithm, ln Consider the flow of liquid water
though a pipe made of stainless steel. The roughness of the pipe is and the internal diameter
of the pipe is The flow is considered fully developed and turbulent with an associated Reynolds
number of Estimate the friction factor in this configuration using the Secant method and
considering the initial guesses of and Show iterations of the Secant method.
Compute the absolute relative approximate percentage error at the end of each iteration. Use at least
significant digits and rounding in all your calculations. Provide a plot of the equation, showing labels and
highlighting the solution of the equation. You are allowed to use MATLAB to create the plot.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


