Question: 2 A B Problem 3 (30 points) 1. (5 points) Run Dijkstra's algorithm on the graph on the right starting at node A. Use a
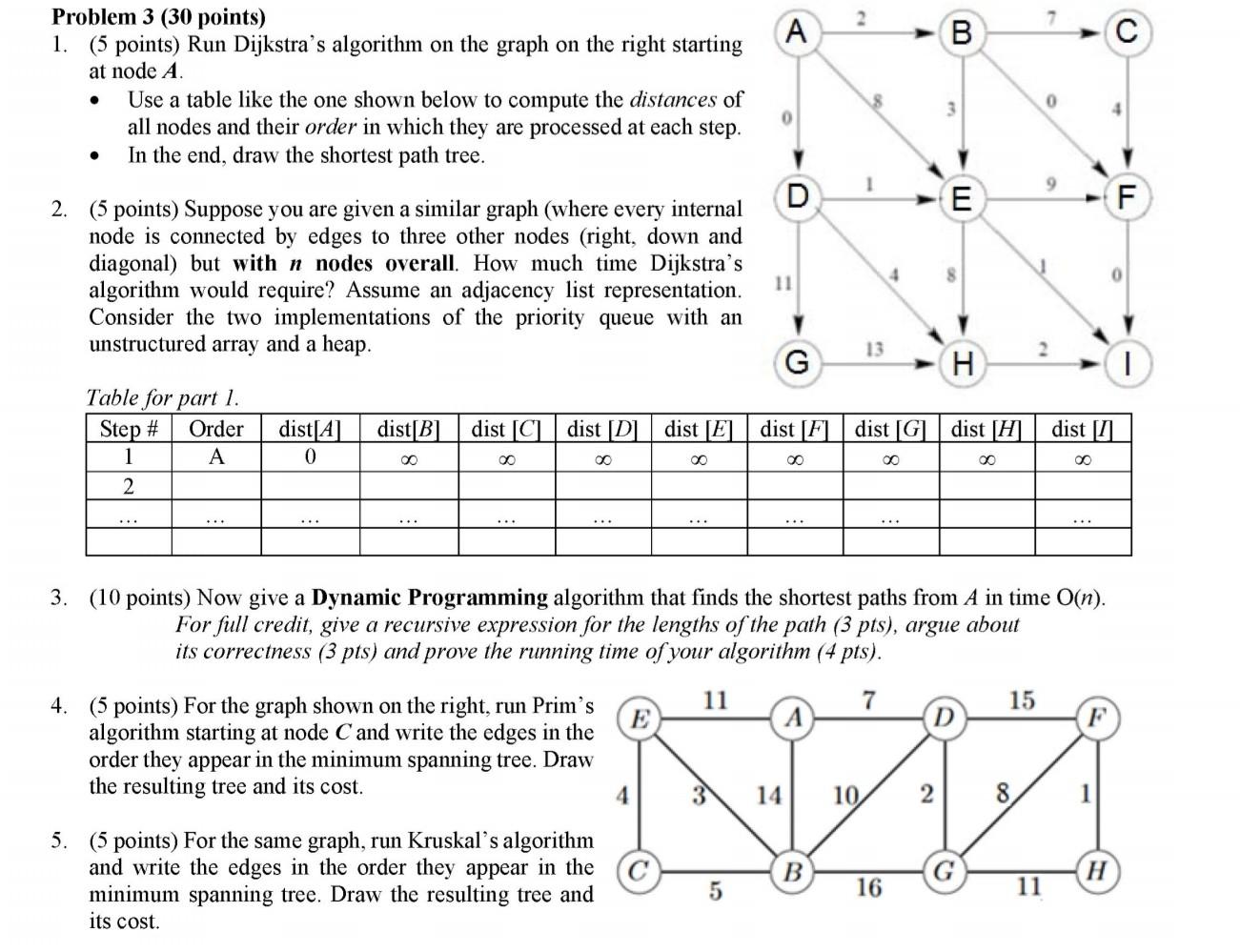
2 A B Problem 3 (30 points) 1. (5 points) Run Dijkstra's algorithm on the graph on the right starting at node A. Use a table like the one shown below to compute the distances of all nodes and their order in which they are processed at each step. In the end, draw the shortest path tree. . D E F 2. (5 points) Suppose you are given a similar graph (where every internal node is connected by edges to three other nodes (right, down and diagonal) but with n nodes overall. How much time Dijkstra's algorithm would require? Assume an adjacency list representation. Consider the two implementations of the priority queue with an unstructured array and a heap. 11 13 G H 1 Table for part 1. Order 1 A Step # dist[A] dist[B] dist [C] dist [D] dist [E]dist [F] dist [G]dist |H| dist | 0 2 3. (10 points) Now give a Dynamic Programming algorithm that finds the shortest paths from A in time O(n). For full credit, give a recursive expression for the lengths of the path (3 pts), argue about its correctness (3 pts) and prove the running time of your algorithm (4 pts). 11 7 15 A D F 4. (5 points) For the graph shown on the right, run Prim's algorithm starting at node C and write the edges in the order they appear in the minimum spanning tree. Draw the resulting tree and its cost. 14 10 2 8 1 5. (5 points) For the same graph, run Kruskal's algorithm and write the edges in the order they appear in the minimum spanning tree. Draw the resulting tree and B () 5 16 11 its cost
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


