Question: (2) (a) For the charge configuration shown below, draw eight electric field lines. Then draw a Gaussian surface that encloses both positive charges. What is

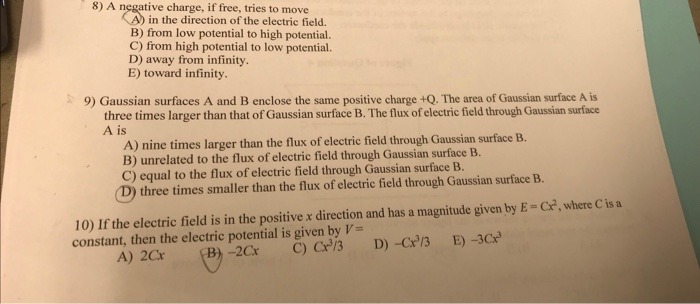

(2) (a) For the charge configuration shown below, draw eight electric field lines. Then draw a Gaussian surface that encloses both positive charges. What is the net number of electric field lines exiting the Gaussian surface minus the net number entering the Gaussian surface? (b) Repeat part (a) except with a Gaussian surface that encloses just the negative charge. (c) Repeat part (a) except with a Gaussian surface that encloses all three charges. -2q + 9 + 98) A negative charge. if free, tries to move A) in the direction of the electric field. B) from low potential to high potential. C) from high potential to low potential. D) away from infinity. E) toward infinity. 9) Gaussian surfaces A and B enclose the same positive charge +Q. The area of Gaussian surface A is three times larger than that of Gaussian surface B. The flux of electric field through Gaussian surface A is A) nine times larger than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. B) unrelated to the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. C) equal to the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. "Dj three times smaller than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. 10) If the electric field is in the positive x direction and has a magnitude given by E = Cx, where C is a constant, then the electric potential is given by V = A) 2Cr B) -2Cx C) Ce/3 D) -Cx/3 E) -30x3) Which of the following statements about Gauss's law are correct? (There may be more than one 3) correct choice.) A) The electric flux passing through a Gaussian surface depends only on the amount of charge inside that surface, not on its size or shape. B) If there is no charge inside of a Gaussian surface, the electric field must be zero at points of that surface. C) Only charge enclosed within a Gaussian surface can produce an electric field at points on that surface. D) Gauss's law is valid only for symmetric charge distributions, such as spheres and cylinders. E) If a Gaussian surface is completely inside an electrostatic conductor, the electric field must always be zero at all points on that surface
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


