Question: 2 C D 1 9 9 4 7 7 B A E 3 1 2 F (a) Apply Dijkstra's algorithm to the given weighted graph,
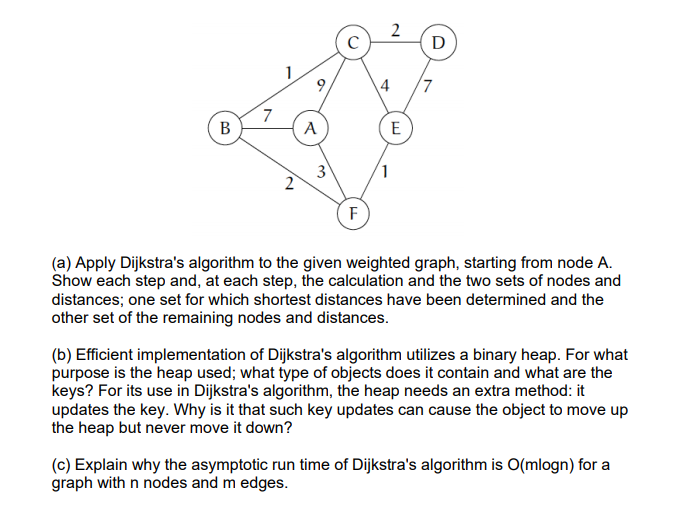
2 C D 1 9 9 4 7 7 B A E 3 1 2 F (a) Apply Dijkstra's algorithm to the given weighted graph, starting from node A. Show each step and, at each step, the calculation and the two sets of nodes and distances; one set for which shortest distances have been determined and the other set of the remaining nodes and distances. (b) Efficient implementation of Dijkstra's algorithm utilizes a binary heap. For what purpose is the heap used; what type of objects does it contain and what are the keys? For its use in Dijkstra's algorithm, the heap needs an extra method: it updates the key. Why is it that such key updates can cause the object to move up the heap but never move it down? (c) Explain why the asymptotic run time of Dijkstra's algorithm is O(mlogn) for a graph with n nodes and m edges. 2 C D 1 9 9 4 7 7 B A E 3 1 2 F (a) Apply Dijkstra's algorithm to the given weighted graph, starting from node A. Show each step and, at each step, the calculation and the two sets of nodes and distances; one set for which shortest distances have been determined and the other set of the remaining nodes and distances. (b) Efficient implementation of Dijkstra's algorithm utilizes a binary heap. For what purpose is the heap used; what type of objects does it contain and what are the keys? For its use in Dijkstra's algorithm, the heap needs an extra method: it updates the key. Why is it that such key updates can cause the object to move up the heap but never move it down? (c) Explain why the asymptotic run time of Dijkstra's algorithm is O(mlogn) for a graph with n nodes and m edges
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


