Question: 2, Let G = (V,E) be a directed graph with edge weights w : E R (which may be positive, negative, or zero), and let
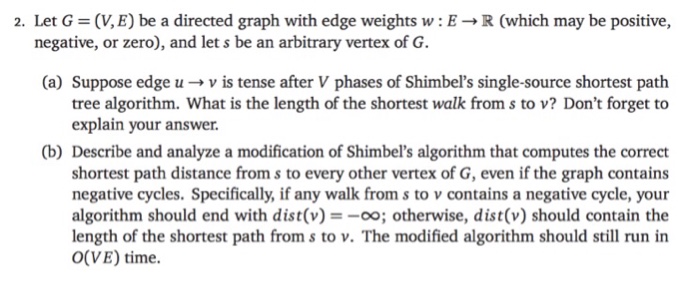
2, Let G = (V,E) be a directed graph with edge weights w : E R (which may be positive, negative, or zero), and let s be an arbitrary vertex of G. (a) Suppose edge u v is tense after V phases of Shimbel's single-source shortest path tree algorithm. What is the length of the shortest walk from s to v? Don't forget to explain your answer (b) Describe and analyze a modification of Shimbel's algorithm that computes the correct shortest path distance from s to every other vertex of G, even if the graph contains negative cycles. Specifically, if any walk from s to v contains a negative cycle, your algorithm should end with dist(v) =-00; otherwise, dist(v) should contain the length of the shortest path from s to v. The modified algorithm should still run in O(VE) time. 2, Let G = (V,E) be a directed graph with edge weights w : E R (which may be positive, negative, or zero), and let s be an arbitrary vertex of G. (a) Suppose edge u v is tense after V phases of Shimbel's single-source shortest path tree algorithm. What is the length of the shortest walk from s to v? Don't forget to explain your answer (b) Describe and analyze a modification of Shimbel's algorithm that computes the correct shortest path distance from s to every other vertex of G, even if the graph contains negative cycles. Specifically, if any walk from s to v contains a negative cycle, your algorithm should end with dist(v) =-00; otherwise, dist(v) should contain the length of the shortest path from s to v. The modified algorithm should still run in O(VE) time
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


