Question: 2. Prepare an excel sheet for example 2.3 to calculate the ionic strength for C. Also, determine the minimum solubility of calcium if K.p -
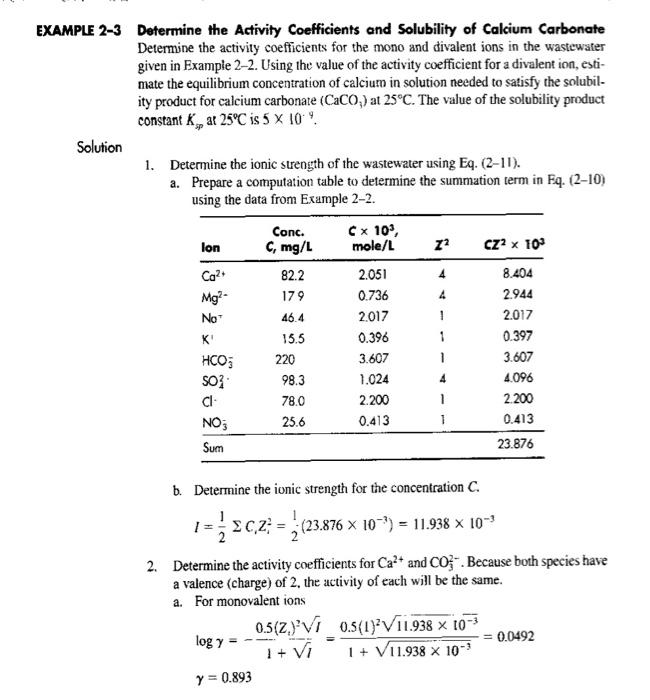

2. Prepare an excel sheet for example 2.3 to calculate the ionic strength for C. Also, determine the minimum solubility of calcium if K.p - 7x109 EXAMPLE 2-3 Determine the Activity Coefficients and Solubility of Calcium Carbonate Determine the activity coefficients for the mono and divalent ions in the wastewater given in Example 2-2. Using the value of the activity coefficient for a divalent ion, esti- mate the equilibrium concentration of calcium in solution needed to satisfy the solubil- ity product for calcium carbonate (CaCO,) at 25C. The value of the solubility product constant K,, at 25C is 5 x 10 Solution 1. Determine the ionic strength of the wastewater using Eq. (2-11). a. Prepare a computation table to determine the summation term in Eq. (2-10) using the data from Example 2-2. Conc. Cx 105, lon $, mg/ mole/L 72 CZ2 x 103 Ca2 82.2 2.051 8.404 Mg?- 179 0.736 2.944 No 46.4 2017 ! 2017 K 15.5 0.396 1 0.397 HCO; 220 3.607 1 3.607 SO? 98.3 1.024 4.096 CI 78.0 2.200 1 2.200 NO; 25.6 0.413 0.413 23.876 4 4 4 Sum b. Determine the ionic strength for the concentration C. 1= $c2 = (23876 x 10) = 11.938 x 10*% - 2. Determine the activity coefficients for Ca+ and Co-. Because both species have a valence (charge) of 2, the activity of each will be the same. a. For monovalent ions 0.5(2)VI 0.5(1) V11.938 x 10-3 log y = 0.0492 + Vi 1 + V11.938 X 100 y = 0.893 b. For divalent ions 0.5(Z) VI 0.5(2) V11.938 x 10-3 logy itvi -0.1968 1 + V11.938 x 10- y = 0.636 3. Determine the minimum solubility of calcium using Eq. (2-15). a. Because the molar concentrations of calcium and carbonate ions are the same. Eq (2-15) can be written as follows: 7C] = kg b. Solve for the concentration C. = Ky 5 X 100 C= y? 11.1 X 10 role/L (0.636) c. Convert the molar concentration of calcium carbonate to mg/L. Ca = 11.1 X 10-3 mole/L x 40,000 mg/mole = 4.45 mg/L
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


