Question: 2. Suppose a network exchange theory experiment is run on the graph depicted in Fig. ure 12.11 (i.e. a graph that is a 3-node path),
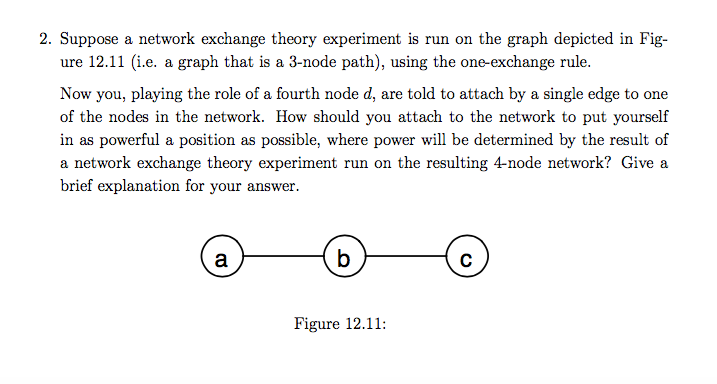
2. Suppose a network exchange theory experiment is run on the graph depicted in Fig. ure 12.11 (i.e. a graph that is a 3-node path), using the one-exchange rule. Now you, playing the role of a fourth node d, are told to attach by a single edge to one of the nodes in the network. How should you attach to the network to put yourself in as powerful a position as possible, where power will be determined by the result of a network exchange theory experiment run on the resulting 4-node network? Give a brief explanation for your answer. Figure 12.11: 2. Suppose a network exchange theory experiment is run on the graph depicted in Fig. ure 12.11 (i.e. a graph that is a 3-node path), using the one-exchange rule. Now you, playing the role of a fourth node d, are told to attach by a single edge to one of the nodes in the network. How should you attach to the network to put yourself in as powerful a position as possible, where power will be determined by the result of a network exchange theory experiment run on the resulting 4-node network? Give a brief explanation for your answer. Figure 12.11
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


