Question: 2. The current zero rates (p.a. continuously compounded) are as follows. Maturity (years) Rate (%) 1 4.0 2 3 4 5 7 10 30 4.5
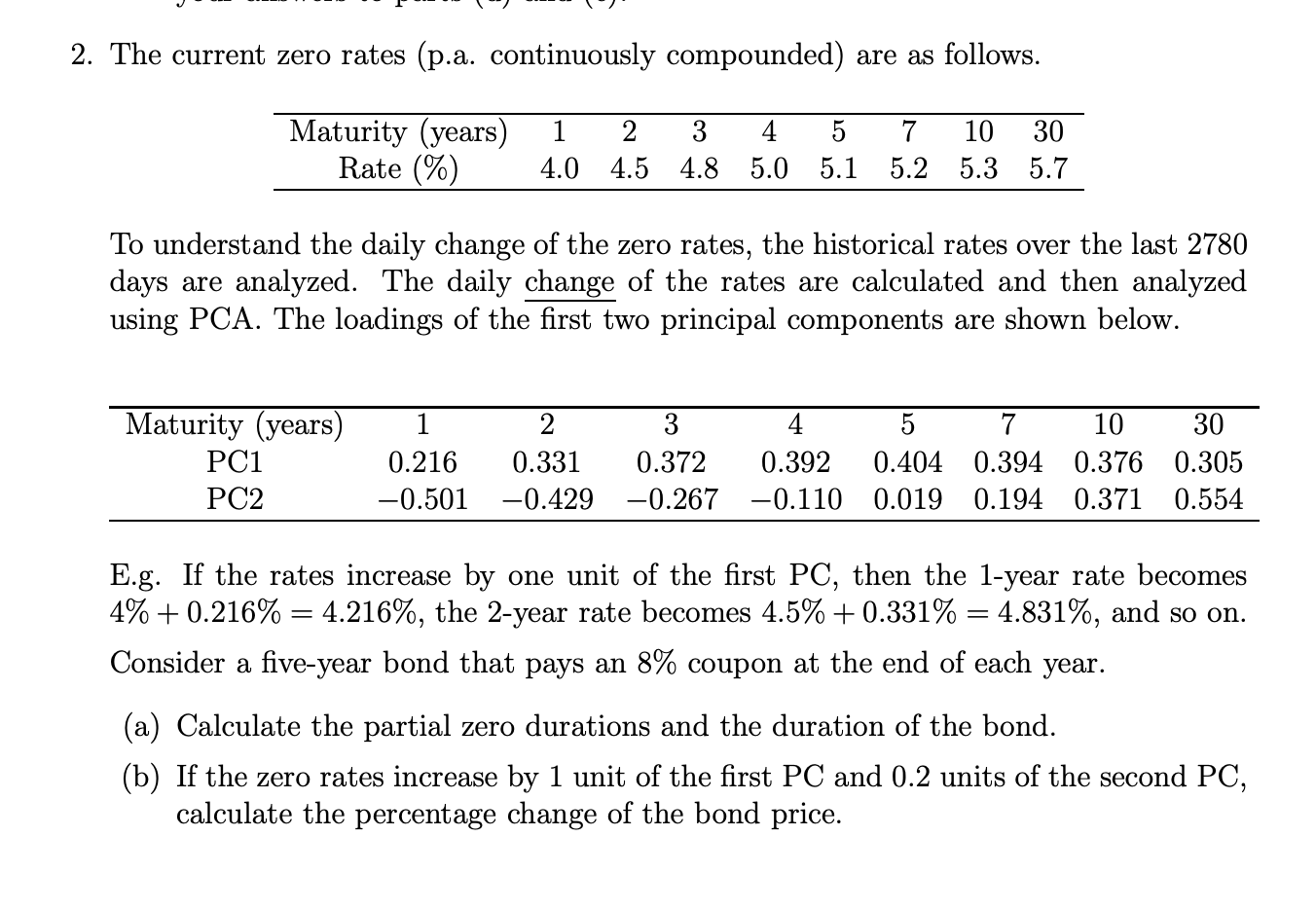
2. The current zero rates (p.a. continuously compounded) are as follows. Maturity (years) Rate (%) 1 4.0 2 3 4 5 7 10 30 4.5 4.8 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.7 To understand the daily change of the zero rates, the historical rates over the last 2780 days are analyzed. The daily change of the rates are calculated and then analyzed using PCA. The loadings of the first two principal components are shown below. Maturity (years) PC1 PC2 1 2 0.216 0.331 -0.501 -0.429 3 4 5 7 10 30 0.372 0.392 0.404 0.394 0.376 0.305 -0.267 -0.110 0.019 0.194 0.371 0.554 E.g. If the rates increase by one unit of the first PC, then the 1-year rate becomes 4% +0.216% = 4.216%, the 2-year rate becomes 4.5% + 0.331% = 4.831%, and so on. Consider a five-year bond that pays an 8% coupon at the end of each year. (a) Calculate the partial zero durations and the duration of the bond. (b) If the zero rates increase by 1 unit of the first PC and 0.2 units of the second PC, calculate the percentage change of the bond price. 2. The current zero rates (p.a. continuously compounded) are as follows. Maturity (years) Rate (%) 1 4.0 2 3 4 5 7 10 30 4.5 4.8 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.7 To understand the daily change of the zero rates, the historical rates over the last 2780 days are analyzed. The daily change of the rates are calculated and then analyzed using PCA. The loadings of the first two principal components are shown below. Maturity (years) PC1 PC2 1 2 0.216 0.331 -0.501 -0.429 3 4 5 7 10 30 0.372 0.392 0.404 0.394 0.376 0.305 -0.267 -0.110 0.019 0.194 0.371 0.554 E.g. If the rates increase by one unit of the first PC, then the 1-year rate becomes 4% +0.216% = 4.216%, the 2-year rate becomes 4.5% + 0.331% = 4.831%, and so on. Consider a five-year bond that pays an 8% coupon at the end of each year. (a) Calculate the partial zero durations and the duration of the bond. (b) If the zero rates increase by 1 unit of the first PC and 0.2 units of the second PC, calculate the percentage change of the bond price
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


