Question: 2. The diffraction pattern below contains the first order diffraction peaks for bec chromium. It was collected using monochromatic radiation having a wavelength of 0.1542
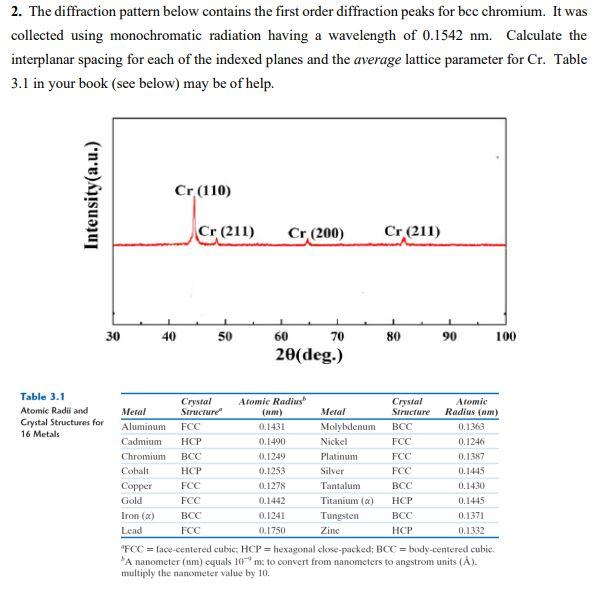
2. The diffraction pattern below contains the first order diffraction peaks for bec chromium. It was collected using monochromatic radiation having a wavelength of 0.1542 nm. Calculate the interplanar spacing for each of the indexed planes and the average lattice parameter for Cr. Table 3.1 in your book (see below) may be of help. Intensity(a.u.) Cr (110) Cr (211) Cr (200) Cr (211) 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 20(deg.) Table 3.1 Atomic Radii and Crystal Structures for 16 Metals Meral Aluminum Cadmium Chromium Cobalt Copper Gold Iron () Lend Crystal Structure FCC HCP BCC HCP FCC FCC BCC FCC Atomic Radius (nm) 0.1431 0.1490 0.1249 0.1253 0.1278 0.1442 0.1241 0.1750 Metal Molybdenum Nickel Platinum Silver Tantalum Titanium (a) Tungsten Zinc Crystal Structure BCC FCC FCC FCC BCC HCP BCC HCP Atomic Radius (nm) 0.1363 0.1246 0.1387 0.1445 0.1430 0.1445 0.1371 0.1.132 "FCC = face-centered cubic HCP = hexagonal close-packed; BCC = body-centered cubic. A nanometer (nm) equals 10m; to convert from nanometers to angstrom units (A). multiply the nanometer value by 10
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


