Question: 2.10 2.10 Nature randomly selects player 1's type, either L or H with probability 1/2 each. Player 1 observes his type and chooses an action
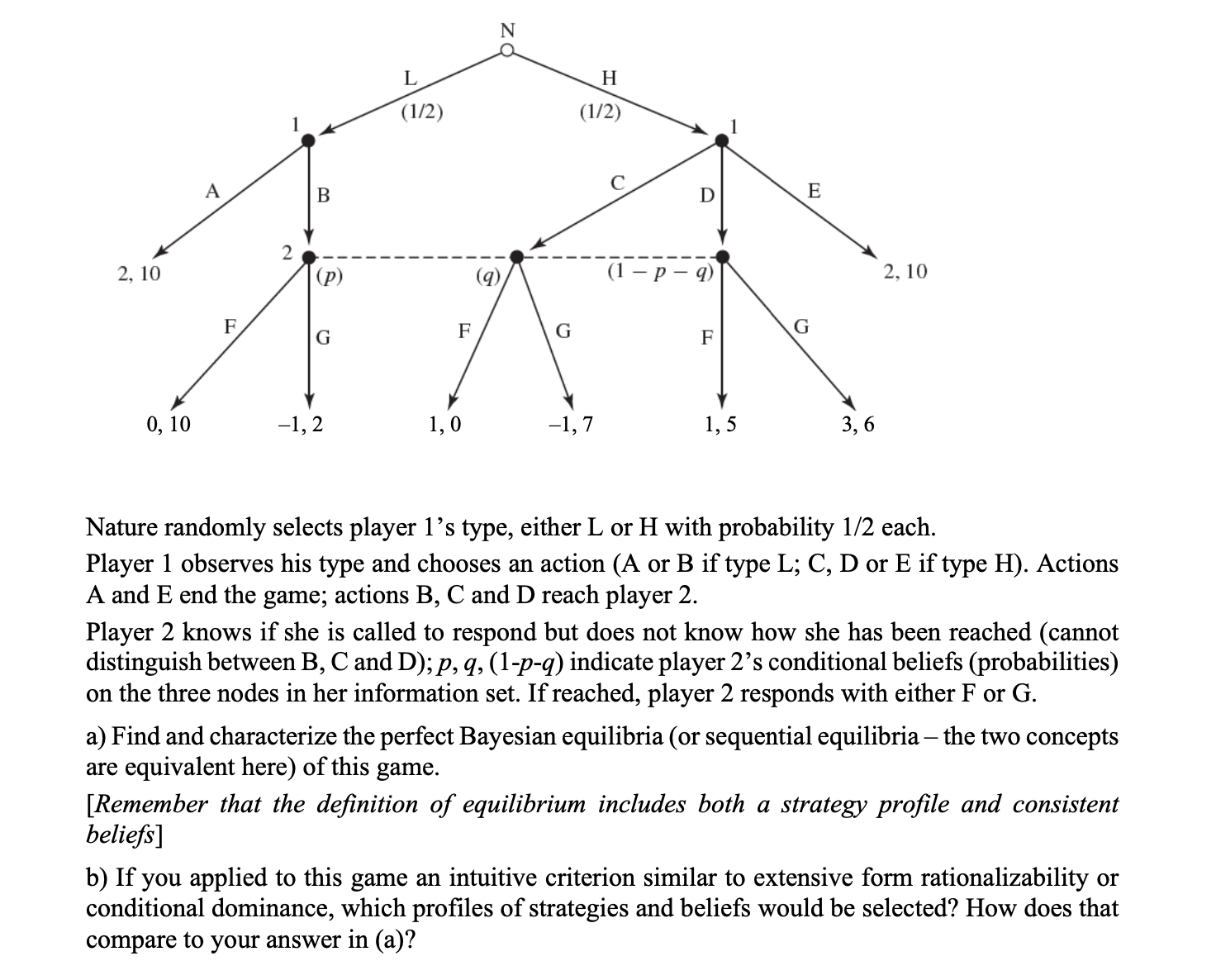
2.10 2.10 Nature randomly selects player 1's type, either L or H with probability 1/2 each. Player 1 observes his type and chooses an action (A or B if type L; C, D or E if type H). Actions A and E end the game; actions B, C and D reach player 2. Player 2 knows if she is called to respond but does not know how she has been reached (cannot distinguish between B, C and D); p, q, (l-p-q) indicate player 2's conditional beliefs (probabilities) on the three nodes in her information set. If reached, player 2 responds with either F or G. a) Find and characterize the perfect Bayesian equilibria (or sequential equilibria the two concepts are equivalent here) of this game. [Remember that the denition of equilibrium includes both a strategy prole and consistent beliefs] b) If you applied to this game an intuitive criterion similar to extensive form rationalizability or conditional dominance, which proles of strategies and beliefs would be selected? How does that compare to your answer in (a)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


