Question: 2-5. Use the probit equation (Equation 2-5) to determine the expected fatalities for people exposed for 2 hours to each of the IDLH concentrations of


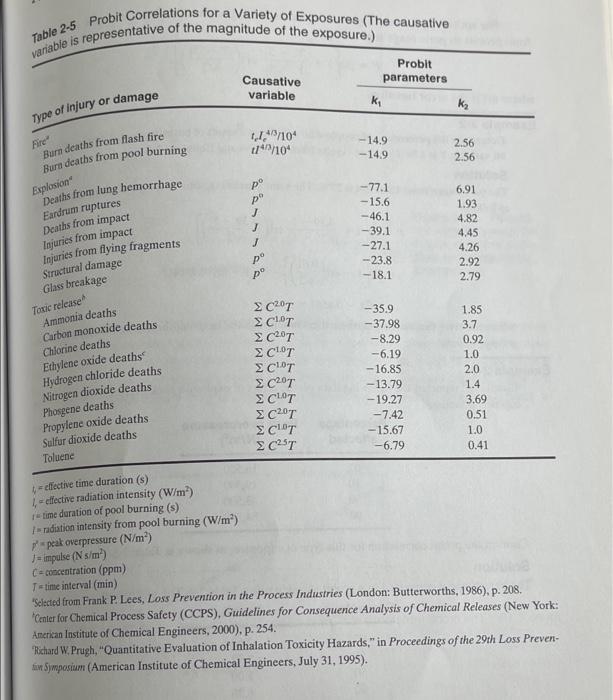
2-5. Use the probit equation (Equation 2-5) to determine the expected fatalities for people exposed for 2 hours to each of the IDLH concentrations of ammonia, chlorine, ethylene oxide, and hydrogen chloride. Table 2-5 lists a variety of probit equations for a number of different types of exposures. The causative factor represents the dose V. The probit variable Y is computed from Y = ki + k, In V. (2-5) variable is representative of the magnitude of the exposure.) Table 2-5 Probit Correlations for a variety of Exposures (The causative Probit parameters Causative variable kt K Type of injury or damage Fire" 11,4%/10 ti4/2/10* - 14.9 -14.9 2.56 2.56 Explosion p p --77.1 -15.6 -46.1 -39.1 -27.1 --23.8 -18.1 6,91 1.93 4.82 4.45 4.26 2.92 2.79 po po Burn deaths from flash fire Bura deaths from pool burning Deaths from lung hemorrhage Fardrum ruptures Deaths from impact Injuries from impact Injuries from flying fragments Structural damage Glass breakage Toxic release Ammonia deaths Carbon monoxide deaths Chlorine deaths Ethylene oxide deaths Hydrogen chloride deaths Nitrogen dioxide deaths Phosgene deaths Propylene oxide deaths Sulfur dioxide deaths Toluenc 1.0 C2.0T -35.9 1.85 C10T -37.98 3.7 c2.0T -8.29 0.92 C1.0T --6.19 C10T -16.85 2.0 C20T -13.79 1.4 C10T -19.27 3.69 C2.0T - 7.42 0.51 Cl0T -15.67 1.0 C25 -6.79 0.41 - effective time duration (3) -effective radiation intensity (W/m") time duration of pool burning (s) 1-radiation intensity from pool burning (W/m?) 1 peak overpressure (N/m) 1 = impulse (Ns/m) C-concentration (ppm) T-time interval (min) 'Selected from Frank P. Lees, Loss Prevention in the Process Industries (London: Butterworths, 1986), p. 208. Center for Chemical Process Safety (CCPS), Guidelines for Consequence Analysis of Chemical Releases (New York: American Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2000), p. 254. Richard W. Prugh, "Quantitative Evaluation of Inhalation Toxicity Hazards," in Proceedings of the 29th Loss Preven- tin Symposium (American Institute of Chemical Engineers, July 31, 1995)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


