Question: 25.69 ... CP Two cylindrical cans with insulating sides and conducting end caps are filled with water, attached to the circuitry shown in Fig.
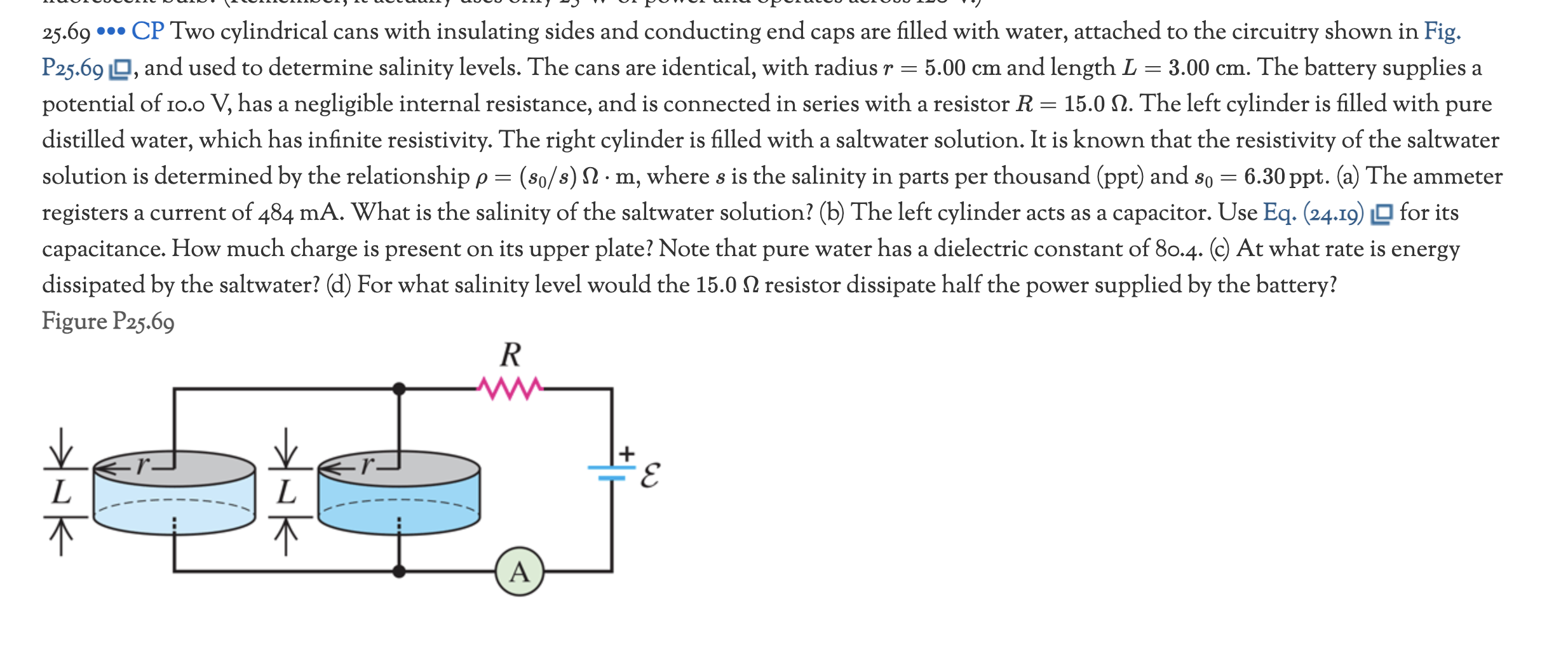
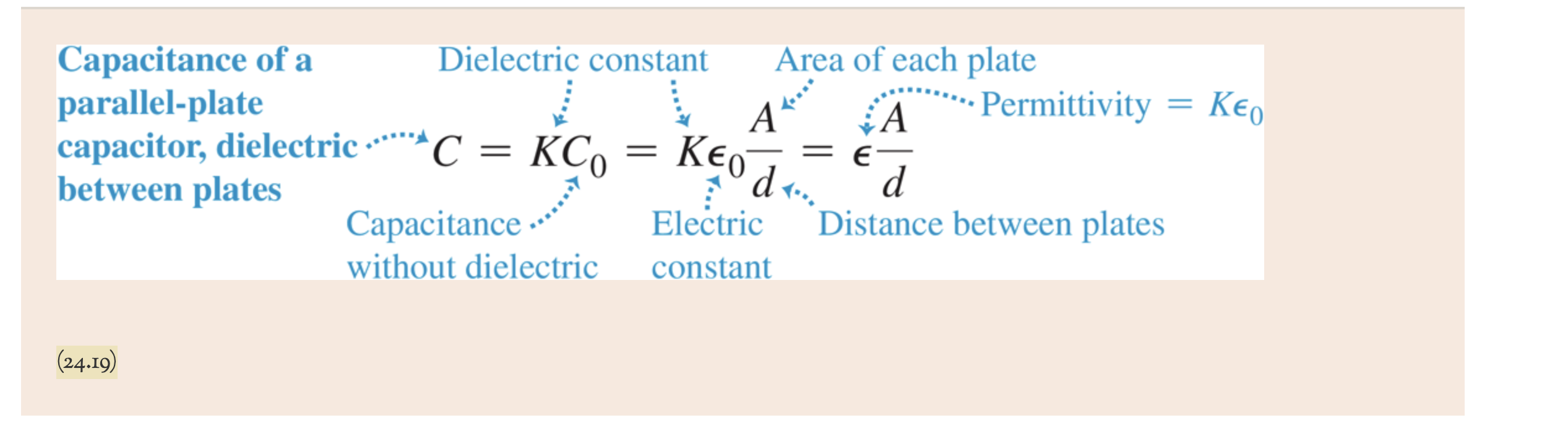
25.69 ... CP Two cylindrical cans with insulating sides and conducting end caps are filled with water, attached to the circuitry shown in Fig. P25.69, and used to determine salinity levels. The cans are identical, with radius r = 5.00 cm and length L = 3.00 cm. The battery supplies a potential of 10.0 V, has a negligible internal resistance, and is connected in series with a resistor R = 15.0 . The left cylinder is filled with pure distilled water, which has infinite resistivity. The right cylinder is filled with a saltwater solution. It is known that the resistivity of the saltwater solution is determined by the relationship p = (80/s) n. m, where s is the salinity in parts per thousand (ppt) and 80 = 6.30 ppt. (a) The ammeter registers a current of 484 mA. What is the salinity of the saltwater solution? (b) The left cylinder acts as a capacitor. Use Eq. (24.19) for its capacitance. How much charge is present on its upper plate? Note that pure water has a dielectric constant of 80.4. (c) At what rate is energy dissipated by the saltwater? (d) For what salinity level would the 15.0 2 resistor dissipate half the power supplied by the battery? Figure P25.69 R www so L r- L -r- A + Capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor, dielectric. between plates Dielectric constant Area of each plate C = KCo = d AN = E- A Permittivity = KEO d Capacitance Electric Distance between plates without dielectric constant (24.19)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
This problem involves a couple of physics concepts related to electrical conductivity and capacitance Lets break down each part of the problem step by ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


