Question: 2(b). (20 marks) Figure Q2(b) shows a vertically mounted converging pipe which carries water. The water flows in the positive y-direction and a mesh of
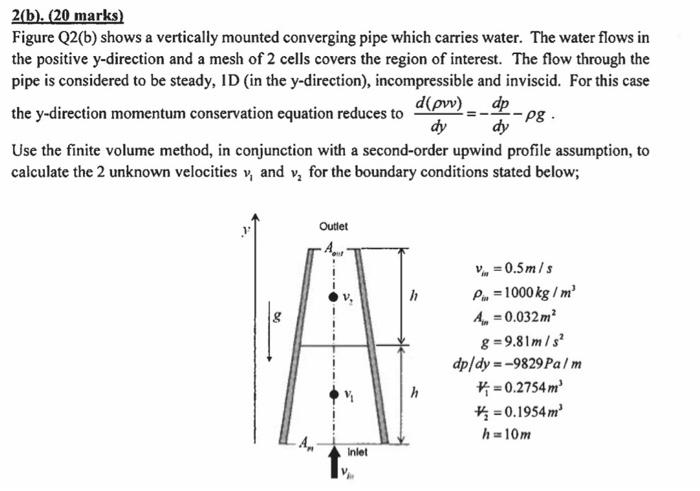
2(b). (20 marks) Figure Q2(b) shows a vertically mounted converging pipe which carries water. The water flows in the positive y-direction and a mesh of 2 cells covers the region of interest. The flow through the pipe is considered to be steady, ID (in the y-direction), incompressible and inviscid. For this case the y-direction momentum conservation equation reduces to d(pv), dp dy -pg dy Use the finite volume method, in conjunction with a second-order upwind profile assumption, to calculate the 2 unknown velocities y, and v, for the boundary conditions stated below; Outlet h v=0.5m/s Pu=1000 kg / m 4. =0.032 m2 8 = 9.81m/s? dp/dy = -9829 Palm V = 0.2754 m Vi = 0.1954 m h=10m h Inlet 2(b). (20 marks) Figure Q2(b) shows a vertically mounted converging pipe which carries water. The water flows in the positive y-direction and a mesh of 2 cells covers the region of interest. The flow through the pipe is considered to be steady, ID (in the y-direction), incompressible and inviscid. For this case the y-direction momentum conservation equation reduces to d(pv), dp dy -pg dy Use the finite volume method, in conjunction with a second-order upwind profile assumption, to calculate the 2 unknown velocities y, and v, for the boundary conditions stated below; Outlet h v=0.5m/s Pu=1000 kg / m 4. =0.032 m2 8 = 9.81m/s? dp/dy = -9829 Palm V = 0.2754 m Vi = 0.1954 m h=10m h Inlet
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


