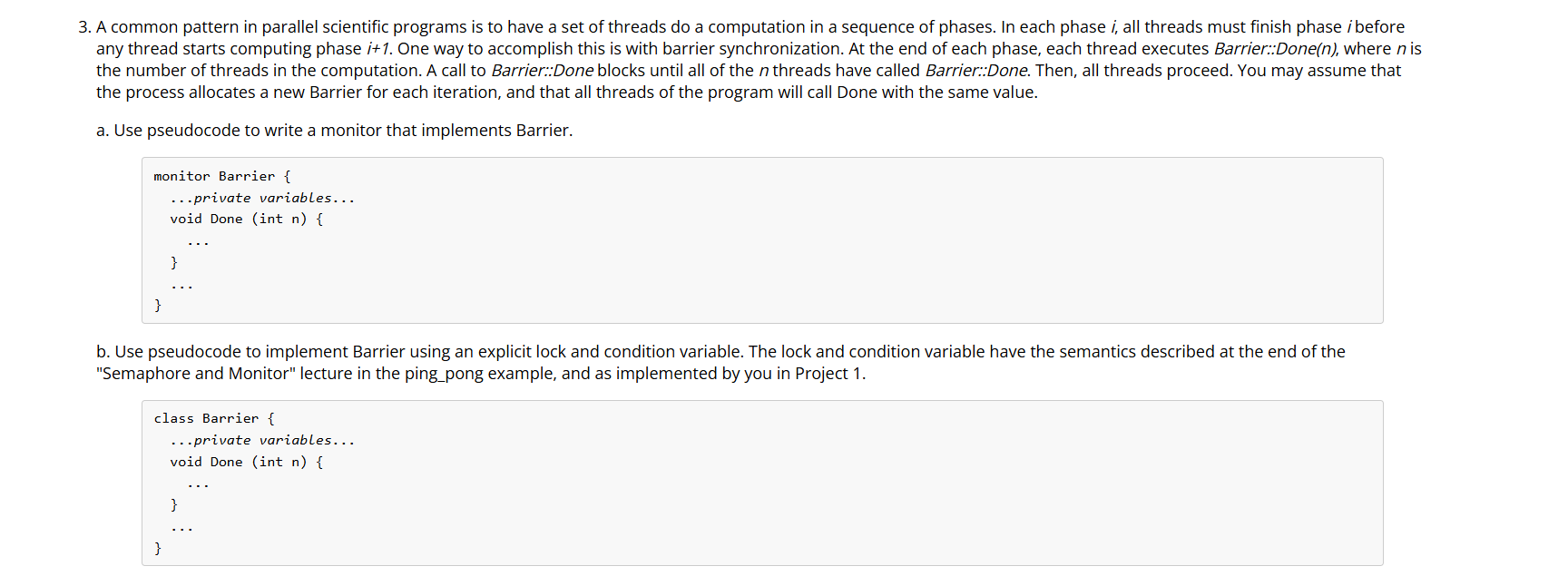
Question: 3 . A common pattern in parallel scientific programs is to have a set of threads do a computation in a sequence of phases. In
A common pattern in parallel scientific programs is to have a set of threads do a computation in a sequence of phases. In each phase i all threads must finish phase i before any thread starts computing phase i One way to accomplish this is with barrier synchronization. At the end of each phase, each thread executes Barrier::Done n where n is the number of threads in the computation. A call to Barrier :: Done blocks until all of the n threads have called Barrier::Done. Then, all threads proceed. You may assume that the process allocates a new Barrier for each iteration, and that all threads of the program will call Done with the same value.
a Use pseudocode to write a monitor that implements Barrier.
monitor Barrier
private variables...
void Done int n
b Use pseudocode to implement Barrier using an explicit lock and condition variable. The lock and condition variable have the semantics described at the end of the "Semaphore and Monitor" lecture in the pingpong example, and as implemented by you in Project
class Barrier
private variables...
void Done int n
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


