Question: 3. A county engineer is conducting a life-cycle cost analysis to determine the feasibility of g a gravel road or leaving it as is. She
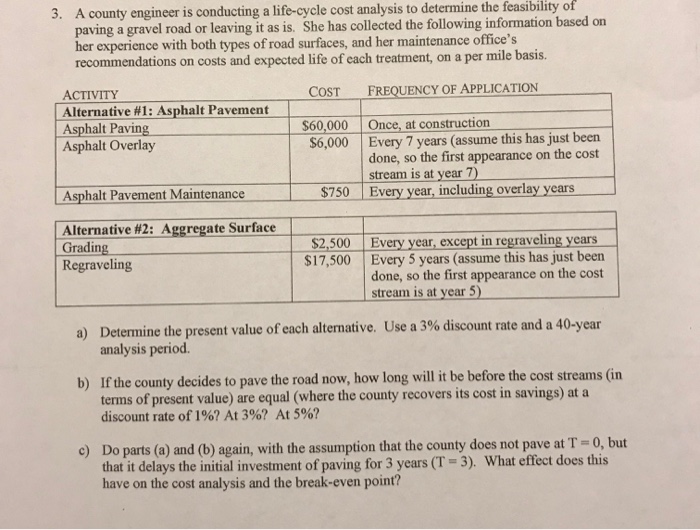
3. A county engineer is conducting a life-cycle cost analysis to determine the feasibility of g a gravel road or leaving it as is. She has collected the following information based on pavin her experience with both types of road surfaces, and her maintenance office's recommendations on costs and expected life of each treatment, on a per mile basis. COST FREQUENCY OF APPLICATION ACTIVITY Alternative #1: Asphalt Pavement Asphalt Paving$ Asphalt Overlay $60,000 Once, at construction S6,000 Every 7 years (assume this has just been done, so the first appearance on the cost stream is at year 7 Every year, including overlay years Asphalt Pavement Maintenance $750 Alternative #2: Aggregatesurface Grading S2,500 Every year, except in regraveling years $17,500 Every 5 years (assume this has just been done, so the first appearance on the cost Regraveling stream is at year 5) Determine the present value of each alternative. Use a 3% discount rate and a 40-year analysis period. a) If the county decides to pave the road now, how long will it be before the cost streams (in terms of present value) are equal (where the county recovers its cost in savings) at a discount rate of 1967 At 3%? At 5%? b) c) Do parts (a) and (b) again, with the assumption that the county does not pave at T-0, but that it delays the initial investment of paving for 3 years (T-3). What effect does this have on the cost analysis and the break-even point
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


