Question: 3. A problem encountered with coupling histidine in protein synthesis is its racemization after activation by DCC. This racemization can be suppressed by protecting the
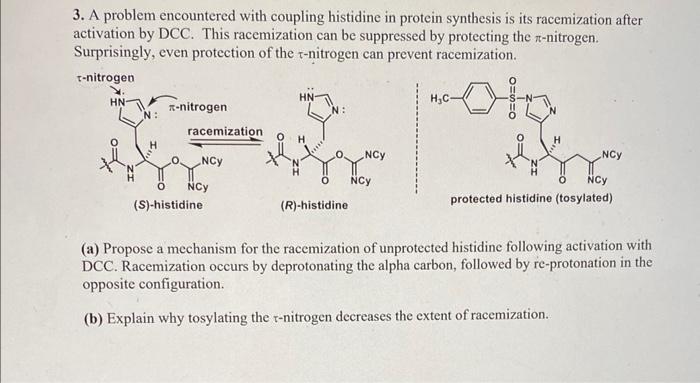
3. A problem encountered with coupling histidine in protein synthesis is its racemization after activation by DCC. This racemization can be suppressed by protecting the -nitrogen. Surprisingly, even protection of the -nitrogen can prevent racemization. -nitrogen (S)-histidine (R)-histidine protected histidine (tosylated) (a) Propose a mechanism for the racemization of unprotected histidine following activation with DCC. Racemization occurs by deprotonating the alpha carbon, followed by re-protonation in the opposite configuration. (b) Explain why tosylating the -nitrogen decreases the extent of racemization
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


