Question: 3. A saltwater solution (3.5 wt% NaCl) is concentrated using a lab-scale evaporation apparatus. The initial volume of the solution is 0.500 L at 20

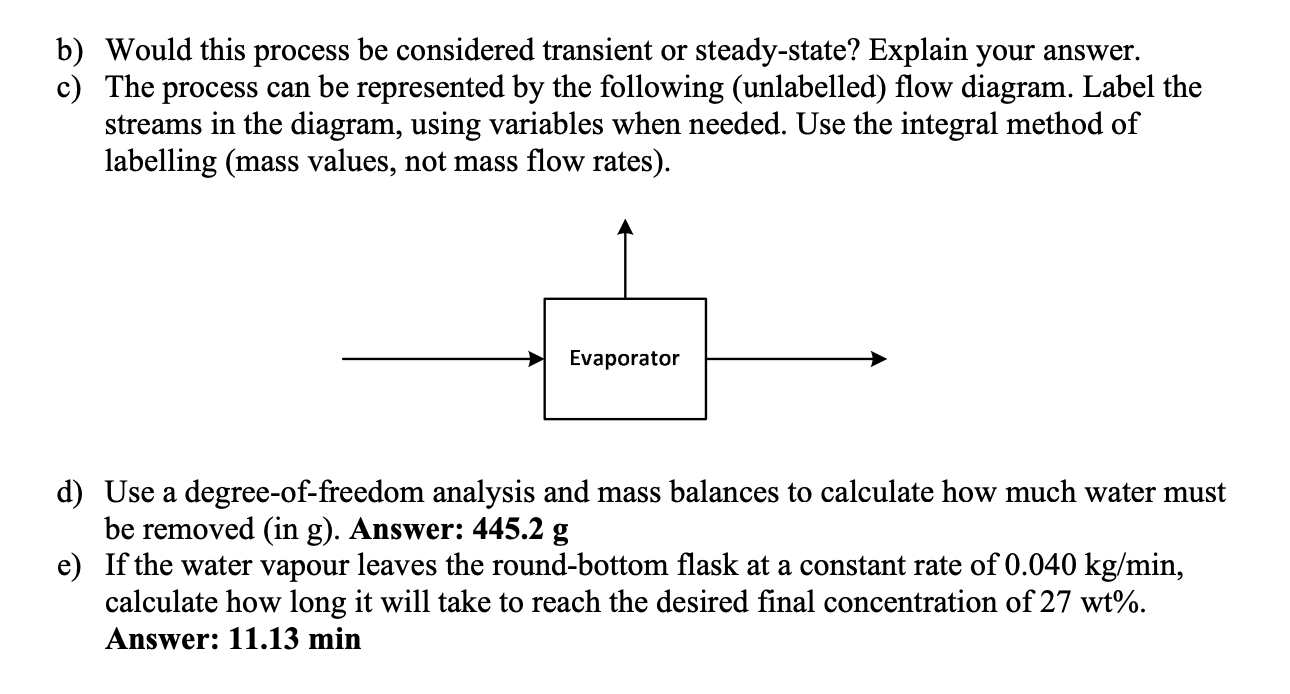
3. A saltwater solution (3.5 wt% NaCl) is concentrated using a lab-scale evaporation apparatus. The initial volume of the solution is 0.500 L at 20 C, where the density of saltwater at this concentration is 1.02301 g/ml. The round-bottom flask containing the solution is heated by a hot plate. The mixture reaches the boiling point, water vapour is formed and leaves the round-bottom flask, and the vapour is condensed and collected in a separate flask. The process is stopped once the solution in the round-bottom flask reaches a concentration of 27 wt% NaCl. For all of the questions below, consider the system to be the round-bottom flask containing the salt solution being concentrated. a) Would this process be considered continuous, batch, or semi-batch? Explain your answer. b) Would this process be considered transient or steady-state? Explain your answer. c) The process can be represented by the following (unlabelled) flow diagram. Label the streams in the diagram, using variables when needed. Use the integral method of labelling (mass values, not mass flow rates). Evaporator d) Use a degree-of-freedom analysis and mass balances to calculate how much water must be removed (in g). Answer: 445.2 g e) If the water vapour leaves the round-bottom flask at a constant rate of 0.040 kg/min, calculate how long it will take to reach the desired final concentration of 27 wt%. Answer: 11.13 min
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


