Question: 3. Adaptive Dynamics: a. Consider the following model for a single population: de = 2 (A - B) where A, B > 0. Do a
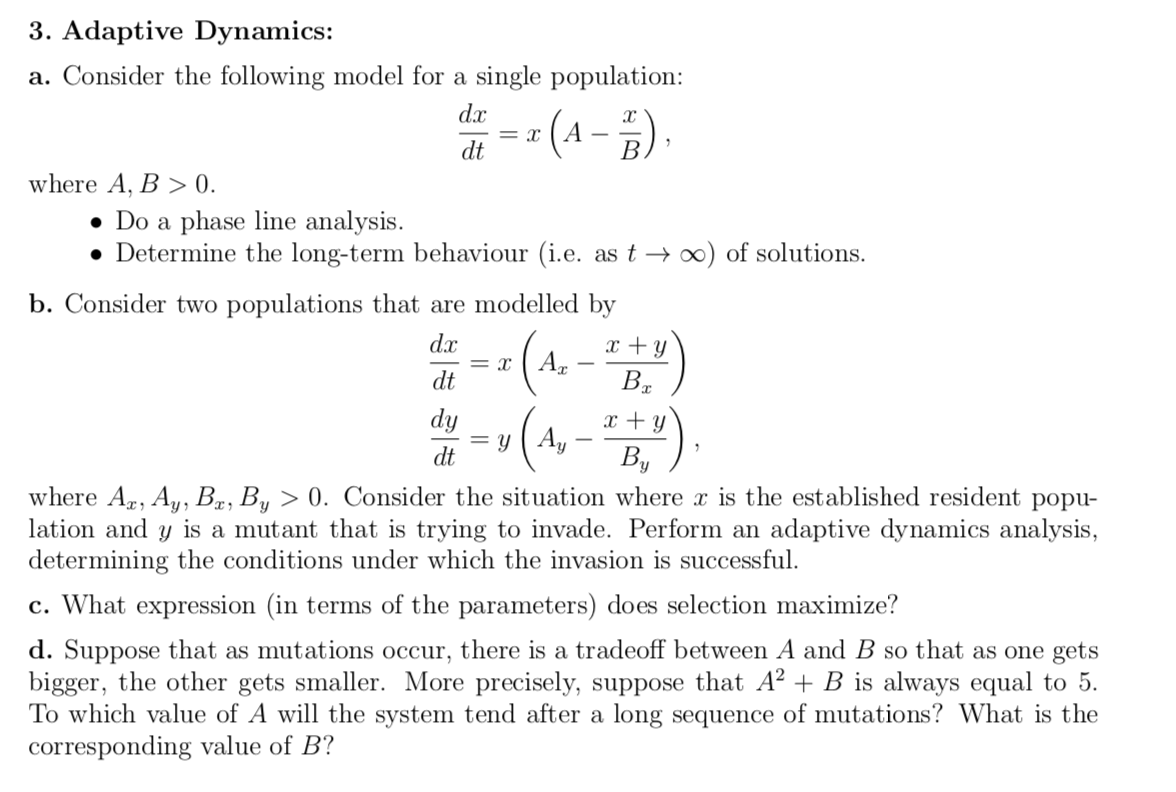
3. Adaptive Dynamics: a. Consider the following model for a single population: de = 2 (A - B) where A, B > 0. Do a phase line analysis. Determine the long-term behaviour (i.e. as t+00) of solutions. b. Consider two populations that are modelled by dr dy y ( A, - By ) dt where Az, Ay, Bx, B, > 0. Consider the situation where x is the established resident popu- lation and y is a mutant that is trying to invade. Perform an adaptive dynamics analysis, determining the conditions under which the invasion is successful. c. What expression (in terms of the parameters) does selection maximize? d. Suppose that as mutations occur, there is a tradeoff between A and B so that as one gets bigger, the other gets smaller. More precisely, suppose that A + B is always equal to 5. To which value of A will the system tend after a long sequence of mutations? What is the corresponding value of B? 3. Adaptive Dynamics: a. Consider the following model for a single population: de = 2 (A - B) where A, B > 0. Do a phase line analysis. Determine the long-term behaviour (i.e. as t+00) of solutions. b. Consider two populations that are modelled by dr dy y ( A, - By ) dt where Az, Ay, Bx, B, > 0. Consider the situation where x is the established resident popu- lation and y is a mutant that is trying to invade. Perform an adaptive dynamics analysis, determining the conditions under which the invasion is successful. c. What expression (in terms of the parameters) does selection maximize? d. Suppose that as mutations occur, there is a tradeoff between A and B so that as one gets bigger, the other gets smaller. More precisely, suppose that A + B is always equal to 5. To which value of A will the system tend after a long sequence of mutations? What is the corresponding value of B
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


