Question: 3. Calculus basics review [Note: helpful for lecture/lab this week & in 2 weeks!] a) What is the time-derivative d/dt of the functions: i) c,
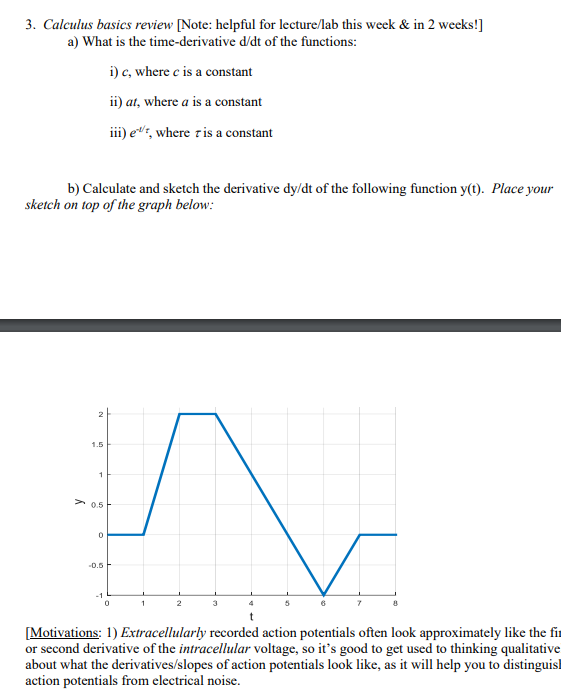
3. Calculus basics review [Note: helpful for lecture/lab this week & in 2 weeks!] a) What is the time-derivative d/dt of the functions: i) c, where c is a constant ii) at, where a is a constant iii) e -t/? , where ? is a constant b) Calculate and sketch the derivative dy/dt of the following function y(t). Place your sketch on top of the graph below: [Motivations: 1) Extracellularly recorded action potentials often look approximately like the first or second derivative of the intracellular voltage, so it's good to get used to thinking qualitatively about what the derivatives/slopes of action potentials look like, as it will help you to distinguish action potentials from electrical noise.
![in 2 weeks!] a) What is the time-derivative d/dt of the functions:](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6665b67dc8781_8856665b67d8e072.jpg)
3. Calculus basics review [Note: helpful for lecture/lab this week & in 2 weeks!] a) What is the time-derivative didt of the functions: i) c, where c is a constant ii) at, where a is a constant iii) ed's, where r is a constant b) Calculate and sketch the derivative dy/dt of the following function y(t). Place your sketch on top of the graph below: 2 D.6 2 [Motivations: 1) Extracellularly recorded action potentials often look approximately like the fi or second derivative of the intracellular voltage, so it's good to get used to thinking qualitative about what the derivatives/slopes of action potentials look like, as it will help you to distinguish action potentials from electrical noise
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


