Question: 3. Consider a 16-bit floating-point representation based on the IEEE floating-point format, with one sign bit, seven exponent bits (k =7), and eight fraction bits

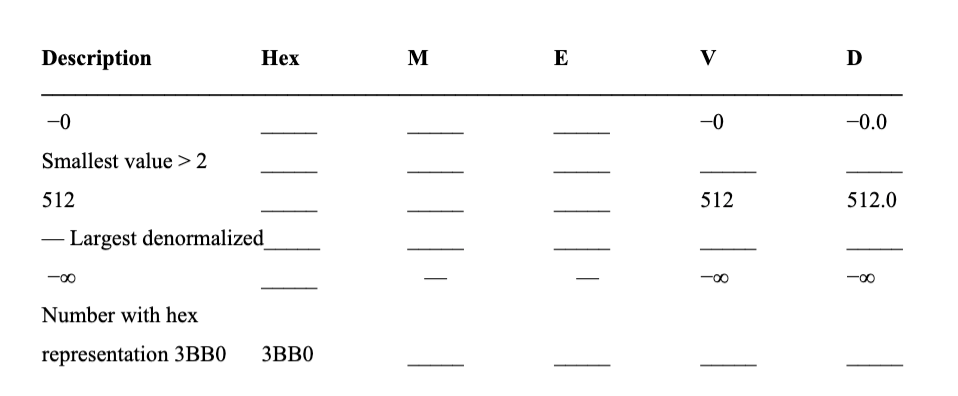
3. Consider a 16-bit floating-point representation based on the IEEE floating-point format, with one sign bit, seven exponent bits (k =7), and eight fraction bits (n=8). The exponent bias is 27-1-1=63. Fill in the table that follows for each of the numbers given, with the following instructions for each column: Hex: The four hexadecimal digits describing the encoded form. M: The value of the significand. This should be a number of the form x or x y, where x is an integer, and y is an integral power of 2. Examples include: 0, 67 64, and 1 256. E: The integer value of the exponent. V: The numeric value represented. Use the notation x or x x2z, where x and z are integers. As an example, to represent the number 78, we would have s =0, M = 74, and E =-1. Our number would therefore have an exponent field of 0x3E (decimal value 631=62) and a significand field 0xC0 (binary 110000002), giving a hex representation 3ECO. You need not fill in entries marked "_". Description Hex M E V D -0 -0 -0.0 Smallest value > 2 512 512 512.0 Largest denormalized Number with hex representation 3BBO 3BBO
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


