Question: 3. Consider the N-step binomial model for the asset price n, n where 0 n SN,0 h S n, and h denotes the number of
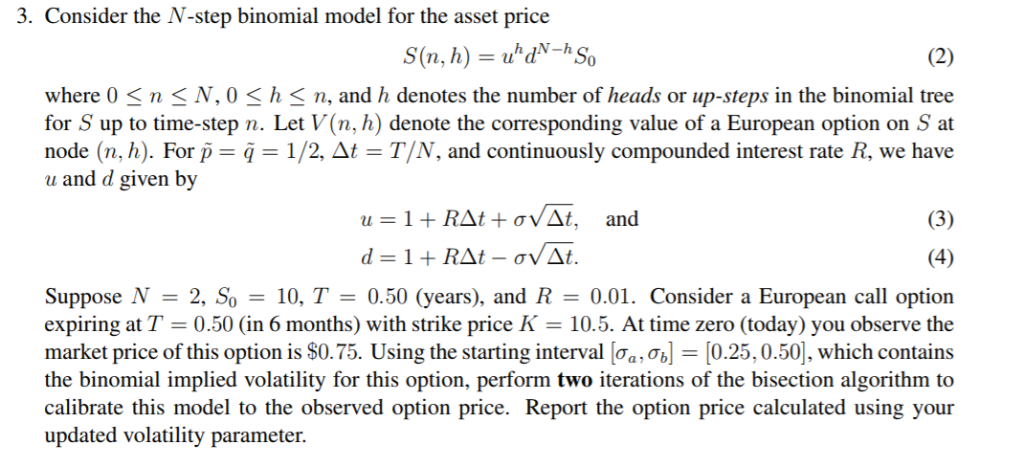
3. Consider the N-step binomial model for the asset price n, n where 0 n SN,0 h S n, and h denotes the number of heads or up-steps in the binomial tree for S up to time-step n. Let V(n, h) denote the corresponding value of a European option on S at node (n, h). For p-q-1/2, -T/N, and continuously compounded interest rate R, we have u and d given by Suppose N-2, So-10, T-0.50 (years), and R-0.01. Consider a European call option expiring at T 0.50 (in 6 months) with strike price K 10.5. At time zero (today) you observe the market price of this option is $0.75 Using the starting interval b = 0.25 0.50 , which contains the binomial implied volatility for this option, perform two iterations of the bisection algorithm to calibrate this model to the observed option price. Report the option price calculated using your updated volatility parameter. 3. Consider the N-step binomial model for the asset price n, n where 0 n SN,0 h S n, and h denotes the number of heads or up-steps in the binomial tree for S up to time-step n. Let V(n, h) denote the corresponding value of a European option on S at node (n, h). For p-q-1/2, -T/N, and continuously compounded interest rate R, we have u and d given by Suppose N-2, So-10, T-0.50 (years), and R-0.01. Consider a European call option expiring at T 0.50 (in 6 months) with strike price K 10.5. At time zero (today) you observe the market price of this option is $0.75 Using the starting interval b = 0.25 0.50 , which contains the binomial implied volatility for this option, perform two iterations of the bisection algorithm to calibrate this model to the observed option price. Report the option price calculated using your updated volatility parameter
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


