Question: 3. Inference about the difference between two population means - Independent samples, population standard deviation unknown Most consumers are not diamond experts, so many rely
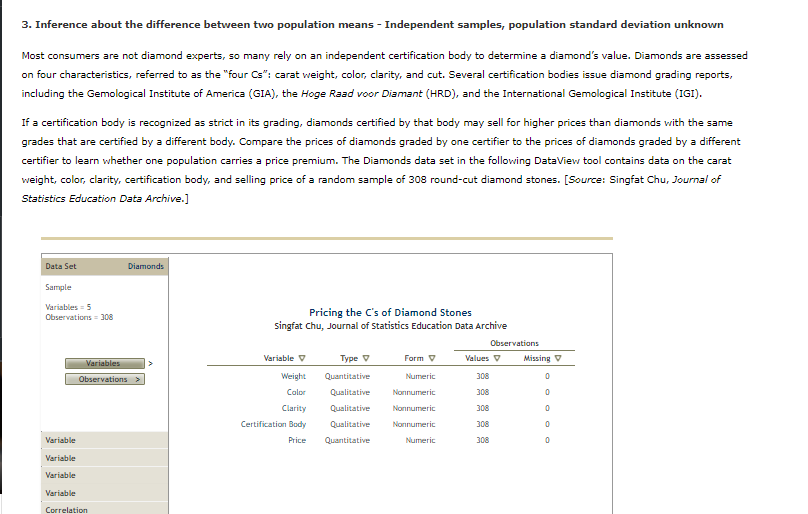
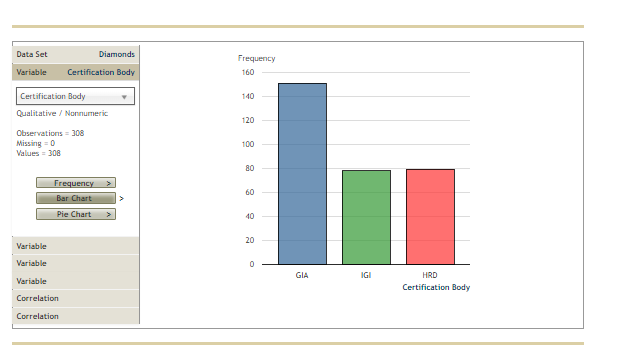
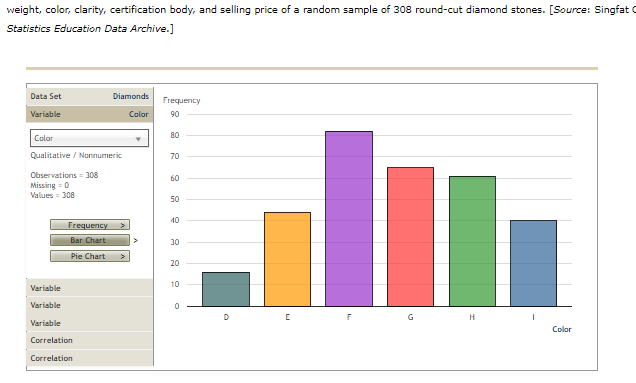

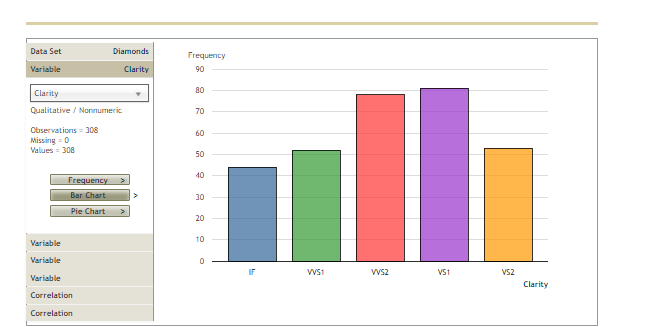
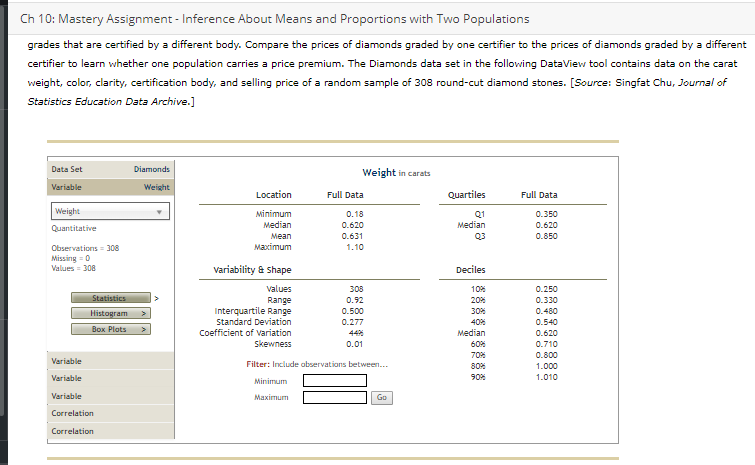
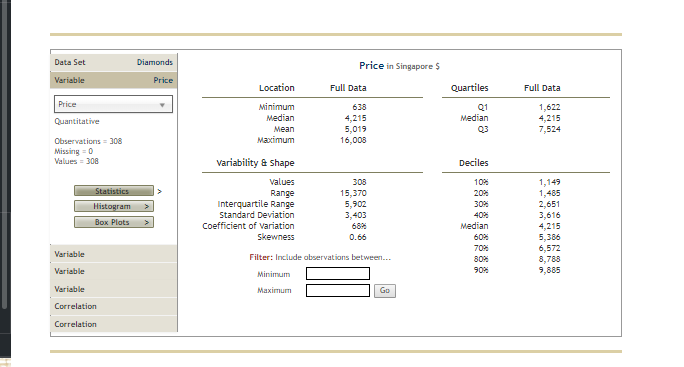
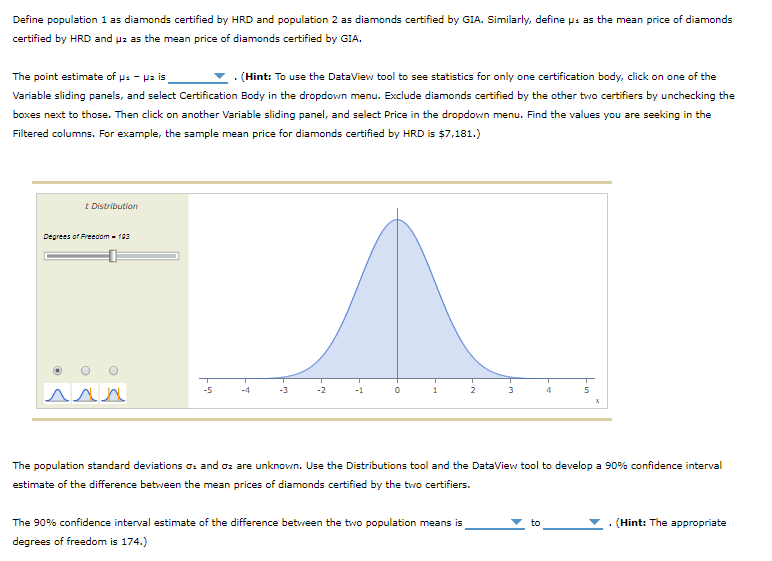
3. Inference about the difference between two population means - Independent samples, population standard deviation unknown Most consumers are not diamond experts, so many rely on an independent certification body to determine a diamond's value. Diamonds are assessed on four characteristics, referred to as the "four Cs": carat weight, color, clarity, and cut. Several certification bodies issue diamond grading reports, including the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), the Hoge Read voor Diamant (HRD), and the International Gemological Institute (IGI). If a certification body is recognized as strict in its grading, diamonds certified by that body may sell for higher prices than diamonds with the same grades that are certified by a different body. Compare the prices of diamonds graded by one certifier to the prices of diamonds graded by a different certifier to learn whether one population carries a price premium. The Diamonds data set in the following DateView tool contains data on the carat weight, color, clarity, certification body, and selling price of a random sample of 308 round-cut diamond stones. [Source: Singfat Chu, Journal of Statistics Education Data Archive.] Data Set Diamonds Sample Variables = 5 Observations = 308 Pricing the C's of Diamond Stones Singfat chu, Journal of Statistics Education Data Archive Observations Variable Type V Form Values Missing Variables Weight Quantitative Numeric 306 Observations Color Qualitative Nonnumeric 308 Clarity Qualitative Nonnumeric 306 Certification Body Qualitative Nonnumeric 308 Variable Price Quantitative Numeric 308 Variable Variable Variable relationData Set Diamonds Frequency Variable Certification Body 160 Certification Body 140 Qualitative / Nonnumeric 120 Observations = 308 Missing = 0 100 Values = 308 Frequency 60 Bar Chart Pie Chart 40 20 Variable Variable GIA IGI HRD Variable Certification Body Correlation Correlationweight, color, clarity, certification body, and selling price of a random sample of 308 round-cut diamond stones. [Source: Singfat Statistics Education Data Archive.] Data Set Diamonds Frequency Variable Color 90 Color Qualitative / Nonnumeric 70 Observations = 308 60 Missing = 0 Values = 308 50 Frequency Bar Chart 30 Pie Chart 20 Variable 10 Variable E F G Variable D Colar Correlation CorrelationBased on your interval estimate, a two-tailed hypothesis test of Ho: : - = = 0 conducted at the 0.10 level of significance would Hor because the value 0 is in the 90% confidence interval estimate of Wi - z. Maybe consumers don't perceive HRD to be stricter in its grading than GIA. It might be the case that prices of diamonds certified by the two certifiers are different because HRD certifies more large diamonds (which sell for higher prices than small diamonds) than GIA. Now redefine : as the mean weight of diamonds certified by HRD and us as the mean weight of diamonds certified by GIA. Using a significance level of a = 0.10, conduct a hypothesis test to determine whether diamonds certified by HRD have a higher mean weight than diamonds certified by GIA. The appropriate degrees of freedom is 201. You conduct test with the null and alternative hypotheses formulated as: O Ho: P: - H2 2 0; Ha: : - H2 0 The value of the test statistic is The p-value is . Therefore, you conclude that diamonds certified by HRD have a higher mean weight than diamonds certified by GIA.Data Set Diamonds Frequency Variable Clarity 90 Clarity Qualitative / Nonnumeric 70 Observations = 308 60 Missing = 0 Values = 308 50 Frequency 40 Bar Chart 30 Pie Chart 20 Variable 10 Variable Variable IF VVS1 VVS2 VS1 V52 Clarity Correlation CorrelationCh 10: Mastery Assignment - Inference About Means and Proportions with Two Populations grades that are certified by a different body. Compare the prices of diamonds graded by one certifier to the prices of diamonds graded by a different certifier to learn whether one population carries a price premium. The Diamonds data set in the following DateView tool contains data on the carat weight, color, clarity, certification body, and selling price of a random sample of 308 round-cut diamond stones. [Source: Singfat Chu, Journal of Statistics Education Data Archive.] Data Set Diamonds Weight in carats Variable Weight Location Full Data Quartiles Full Data Weight Minimum 0.18 Q1 0.350 Quantitative Median 0.620 Median 0.620 LEBW 0.631 03 0.850 Observations = 308 Maximum 1.10 Missing = 0 Values = 308 variability & Shape Deciles values 303 102 0.250 Statistics Range 0.52 20% 0.330 Histogram Interquartile Range 0.500 30% 0.480 0.277 40% 0.540 Box Plots Standard Deviation Coefficient of variation 44 Median 0.620 Skewness 0.01 0.710 70% 0.800 Variable Filter: Include observations between... 1.000 Variable Minimum 90% 1.010 Variable Maximum Go Correlation CorrelationData Set Diamonds Price in Singapore $ Variable Price Location Full Data Quartiles Full Data Price Minimum 638 01 1,622 Quantitative Median 4,215 Median 4,215 Mean 5,019 03 7,524 Observations = 308 Maximum 16,008 Missing = 0 Values = 308 Variability & Shape Deciles values 308 102 1,149 Statistics Range 15,370 1,485 Histogram Interquartile Range 5,902 30M 2,651 Box Plots Standard Deviation 3,403 402 3,616 Coefficient of variation Median 4,215 Skewness D.66 60% 5,386 Variable 6,572 Filter: Include observations between... 80% 8,788 Variable Minimum 90% 9,885 Variable Maximum GO Correlation CorrelationDefine population 1 as diamonds certified by HRD and population 2 as diamonds certified by GIA. Similarly, define wi as the mean price of diamonds certified by HRD and uz as the mean price of diamonds certified by GIA. The point estimate of we - we is . (Hint: To use the DataView tool to see statistics for only one certification body, click on one of the Variable sliding panels, and select Certification Body in the dropdown menu. Exclude diamonds certified by the other two certifiers by unchecking the boxes next to those. Then click on another Variable sliding panel, and select Price in the dropdown menu. Find the values you are seeking in the Filtered columns. For example, the sample mean price for diamonds certified by HRD is $7,181.) t Distribution Degrees of Freedom - 108 O O -5 The population standard deviations : and oz are unknown. Use the Distributions tool and the DateView tool to develop a 90% confidence interval estimate of the difference between the mean prices of diamonds certified by the two certifiers. The 90% confidence interval estimate of the difference between the two population means is to 7 . (Hint: The appropriate degrees of freedom is 174.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


