Question: 3. Measuring stand-alone risk using realized (historical)data Returns earned over a given time period are called realized returns. Historical data on realized returns is often
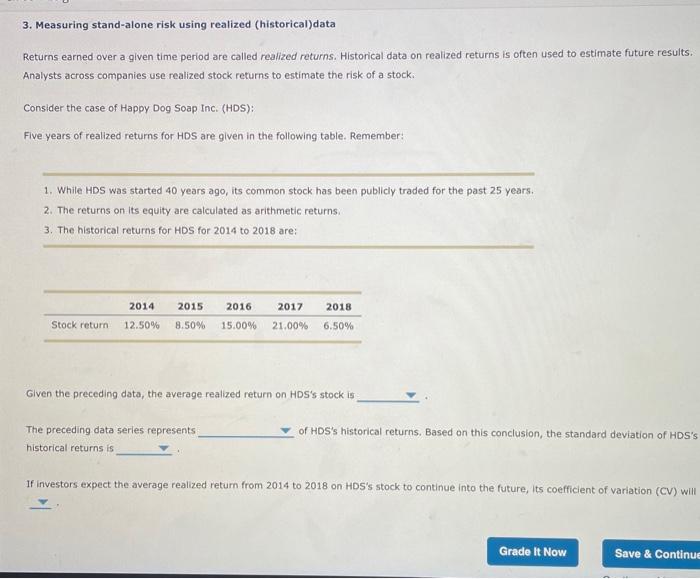
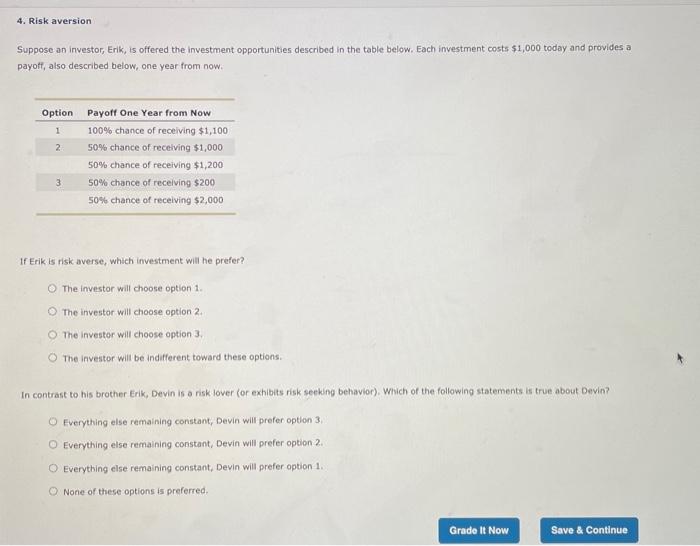
3. Measuring stand-alone risk using realized (historical)data Returns earned over a given time period are called realized returns. Historical data on realized returns is often used to estimate future results. Analysts across companies use realized stock returns to estimate the risk of a stock. Consider the case of Happy Dog Soap Inc. (HDS): Five years of realized returns for HDS are given in the following table. Remember: 1. While HDS was started 40 years ago, its common stock has been publicly traded for the past 25 years. 2. The returns on its equity are calculated as arithmetic returns 3. The historical returns for HDS for 2014 to 2018 are: 2016 2018 2014 12.50% 2015 8.50% 2017 21.00% Stock return 15.00% 6.50% Given the preceding data, the average realized return on HDS's stock is The preceding data series represents historical returns is of HDS's historical returns. Based on this conclusion, the standard deviation of HDS's if investors expect the average realized return from 2014 to 2018 on HDS's stock to continue into the future, its coefficient of variation (CV) will Grade It Now Save & Continue 4. Risk aversion Suppose an investor, Erik, is offered the investment opportunities described in the table below. Each investment costs $1,000 today and provides a payoff, also described below, one year from now. Option 1 2 Payoff One Year from Now 100% chance of receiving $1,100 50% chance of receiving $1,000 50% chance of receiving $1,200 50% chance of receiving $200 50% chance of receiving $2,000 3 If Erik is risk averse, which investment will he prefer? The investor will choose option 1 The investor will choose option 2 The Investor will choose option 3 The investor will be indifferent toward these options In contrast to his brother Erik, Devin is a risk lover (or exhibits risk seeking behavior), which of the following statements is true about Devin? O Everything else remaining constant, Devin will prefer option 3 O Everything else remaining constant, Devin will prefer option 2 O Everything else remaining constant, Devin will prefer option 1. None of these options is preferred Grade It Now Save & Continue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


