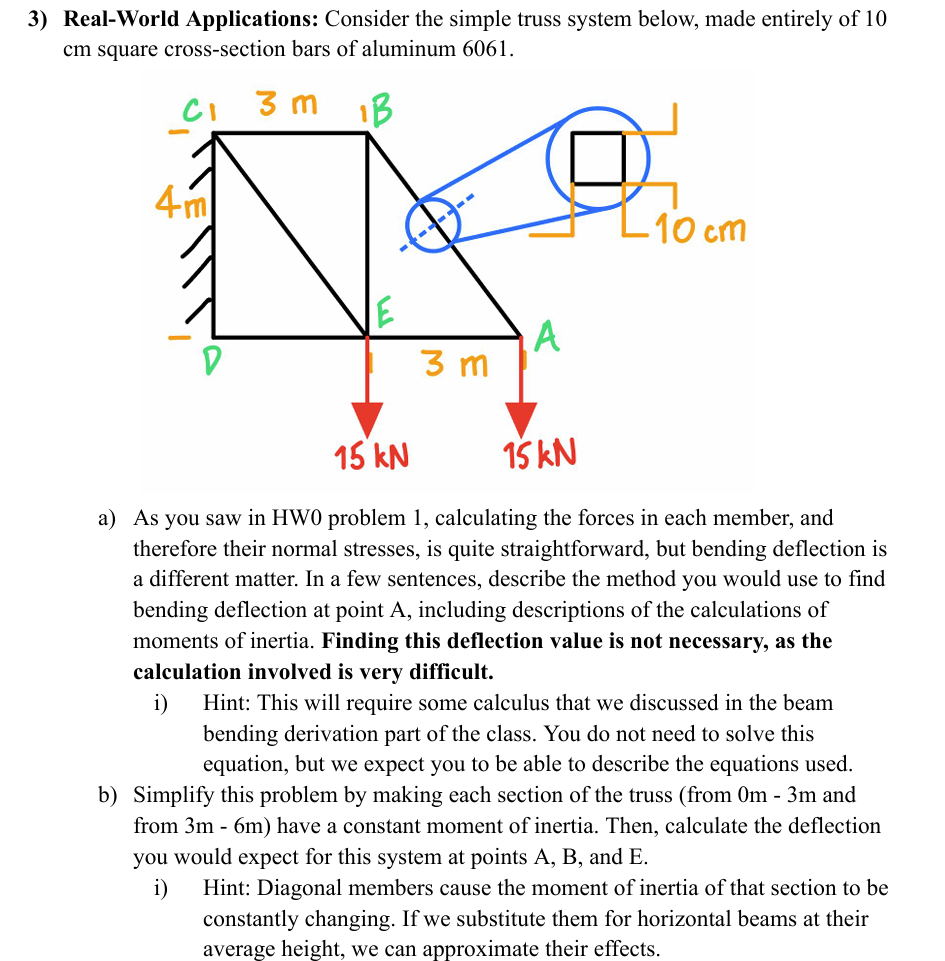
Question: 3 ) Real - World Applications: Consider the simple truss system below, made entirely of 1 0 cm square cross - section bars of aluminum
RealWorld Applications: Consider the simple truss system below, made entirely of cm square crosssection bars of aluminum
a As you saw in HW problem calculating the forces in each member, and therefore their normal stresses, is quite straightforward, but bending deflection is a different matter. In a few sentences, describe the method you would use to find bending deflection at point A including descriptions of the calculations of moments of inertia. Finding this deflection value is not necessary, as the calculation involved is very difficult.
i Hint: This will require some calculus that we discussed in the beam bending derivation part of the class. You do not need to solve this equation, but we expect you to be able to describe the equations used.
b Simplify this problem by making each section of the truss from mathrm~mmathrm~m and from mathrm~mmathrm~m have a constant moment of inertia. Then, calculate the deflection you would expect for this system at points mathrmAmathrmB and E
i Hint: Diagonal members cause the moment of inertia of that section to be constantly changing. If we substitute them for horizontal beams at their average height, we can approximate their effects.
Please calculate the deflection of parts AB and E numerically for part b of the question.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


