Question: 3. SOLVING STOCHASTIC DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (20 POINTS) In this exercise you will solve a stochastic differential equation. Assume you model interest rates with the

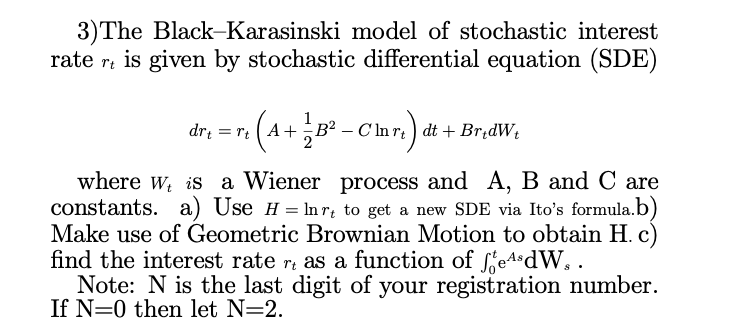

3. SOLVING STOCHASTIC DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (20 POINTS) In this exercise you will solve a stochastic differential equation. Assume you model interest rates with the following mean-reverting stochastic differential equation drt (a Brt)dt + dWt. = (1) Use the Ito formula to derive d(ert). Simplify your formula so that it does not involve rt. (2) Integrate the equation you obtain in (1) and solve for rt. 3)The Black-Karasinski model of stochastic interest rate rt is given by stochastic differential equation (SDE) dr = r; (4+ B - Clar,) dt + BridW, where W is a Wiener process and A, B and C are constants. a) Use H = ln r to get a new SDE via Ito's formula.b) Make use of Geometric Brownian Motion to obtain H. c) find the interest rate rt as a function of AsdW.. Note: N is the last digit of your registration number. If N 0 then let N=2. 12 The Cox-Ingersoll-Ross model of interest rates assumes that the interest rate, r, is not deterministic, but satisfies the stochastic differential equation dr;= (a - Br,) dt + r,dW, where {W,}>0 is standard P-Brownian motion. This process is known as a squared Bessel process. Find the stochastic differential equation followed by {20 in the case = 0. Suppose that {u(t)}>o satisfies the ordinary differential equation du (t) = -Bu(t) di Su(t) - u(t), u(0) = 0, for some constant > 0. Fix T > 0. Assuming still that = 0, for 0 IT find the differential equation satisfied by E[exp(-u(T-1))]. Hence calculate the mean and variance of FT and P[/T = 0].
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


