Question: 3 Step 1: Indicate if the statement is related to cost leadership (C), or Differentiation (D) strategy. Step 2: Indicate if statement is an (S)
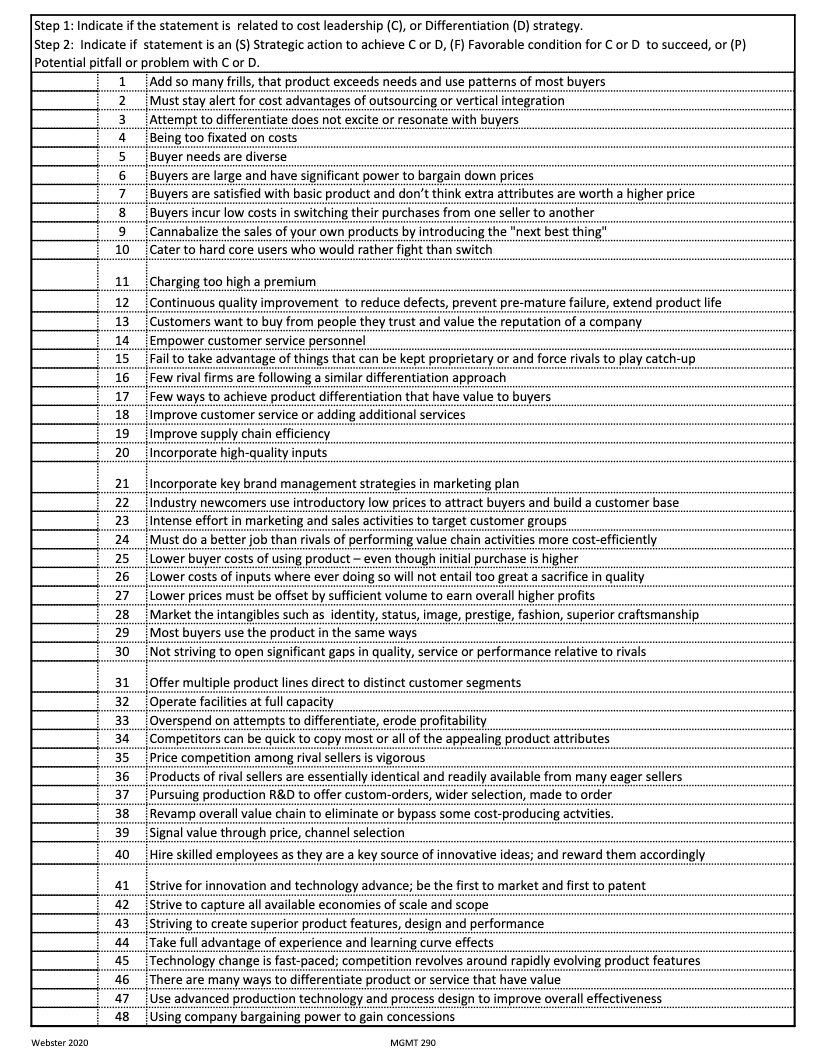
3 Step 1: Indicate if the statement is related to cost leadership (C), or Differentiation (D) strategy. Step 2: Indicate if statement is an (S) Strategic action to achieve C or D, (F) Favorable condition for Cor D to succeed, or (P) Potential pitfall or problem with Cor D. 1 Add so many frills, that product exceeds needs and use patterns of most buyers 2 Must stay alert for cost advantages of outsourcing or vertical integration Attempt to differentiate does not excite or resonate with buyers 4 Being too fixated on costs Buyer needs are diverse Buyers are large and have significant power to bargain down prices 7 Buyers are satisfied with basic product and don't think extra attributes are worth a higher price 8 Buyers incur low costs in switching their purchases from one seller to another Cannabalize the sales of your own products by introducing the "next best thing" 10 Cater to hard core users who would rather fight than switch 5 6 9 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Charging too high a premium Continuous quality improvement to reduce defects, prevent pre-mature failure, extend product life Customers want to buy from people they trust and value the reputation of a company Empower customer service personnel Fail to take advantage of things that can be kept proprietary or and force rivals to play catch-up Few rival firms are following a similar differentiation approach Few ways to achieve product differentiation that have value to buyers Improve customer service or adding additional services Improve supply chain efficiency Incorporate high-quality inputs 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Incorporate key brand management strategies in marketing plan Industry newcomers use introductory low prices to attract buyers and build a customer base Intense effort in marketing and sales activities to target customer groups Must do a better job than rivals of performing value chain activities more cost-efficiently Lower buyer costs of using product - even though initial purchase is higher Lower costs of inputs where ever doing so will not entail too great a sacrifice in quality Lower prices must be offset by sufficient volume to earn overall higher profits Market the intangibles such as identity, status, image, prestige, fashion, superior craftsmanship Most buyers use the product in the same ways Not striving to open significant gaps in quality, service or performance relative to rivals 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 Offer multiple product lines direct to distinct customer segments Operate facilities at full capacity Overspend on attempts to differentiate, erode profitability Competitors can be quick to copy most or all of the appealing product attributes Price competition among rival sellers is vigorous Products of rival sellers are essentially identical and readily available from many eager sellers Pursuing production R&D to offer custom-orders, wider selection, made to order Revamp overall value chain to eliminate or bypass some cost-producing actvities. Signal value through price, channel selection Hire skilled employees as they are a key source of innovative ideas; and reward them accordingly 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 Strive for innovation and technology advance; be the first to market and first to patent Strive to capture all available economies of scale and scope Striving to create superior product features, design and performance Take full advantage of experience and learning curve effects Technology change is fast-paced, competition revolves around rapidly evolving product features There are many ways to differentiate product or service that have value Use advanced production technology and process design to improve overall effectiveness Using company bargaining power to gain concessions Webster 2020 MGMT 290





