Question: 4. (20 pts) One aspect of software-defined data routing is to select a cost-optimal end-to-end path for data transport, where the per-hop link costs
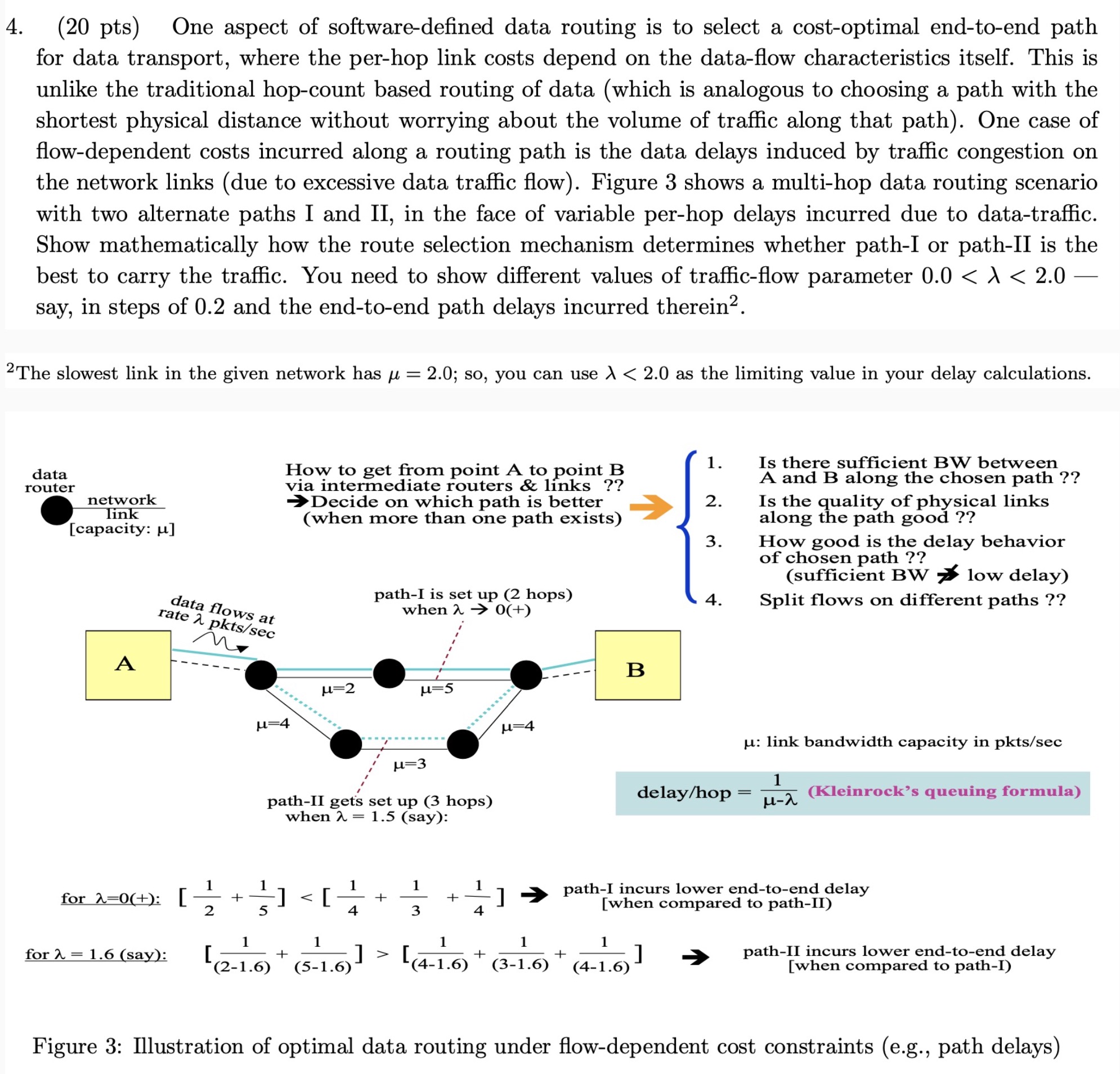
4. (20 pts) One aspect of software-defined data routing is to select a cost-optimal end-to-end path for data transport, where the per-hop link costs depend on the data-flow characteristics itself. This is unlike the traditional hop-count based routing of data (which is analogous to choosing a path with the shortest physical distance without worrying about the volume of traffic along that path). One case of flow-dependent costs incurred along a routing path is the data delays induced by traffic congestion on the network links (due to excessive data traffic flow). Figure 3 shows a multi-hop data routing scenario with two alternate paths I and II, in the face of variable per-hop delays incurred due to data-traffic. Show mathematically how the route selection mechanism determines whether path-I or path-II is the best to carry the traffic. You need to show different values of traffic-flow parameter 0.0 < > < 2.0 say, in steps of 0.2 and the end-to-end path delays incurred therein. 2The slowest link in the given network has = 2.0; so, you can use < 2.0 as the limiting value in your delay calculations. data router network link [capacity: u] A data flows at rate 2 pkts/sec n for =0(+): [ + 2 for 2 1.6 (say): How to get from point A to point B via intermediate routers & links ?? Decide on which path is better (when more than one path exists) =4 H=2 }{} ] [(4-1.6) * (3-1.6) B + 1. 2. 1 ] (4-1.6) 3. 4. delay/hop Is there sufficient BW between A and B along the chosen path ?? Is the quality of physical links along the path good ?? = How good is the delay behavior of chosen path ?? (sufficient BW low delay) Split flows on different paths ?? : link bandwidth capacity in pkts/sec path-I incurs lower end-to-end delay [when compared to path-II) 1 H-A (Kleinrock's queuing formula) path-II incurs lower end-to-end delay [when compared to path-I) Figure 3: Illustration of optimal data routing under flow-dependent cost constraints (e.g., path delays)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


