Question: 4. Consider a surface with M equivalent independent and distinguishable sites of adsorption. This surface is in contact with a large mixture of ideal gases
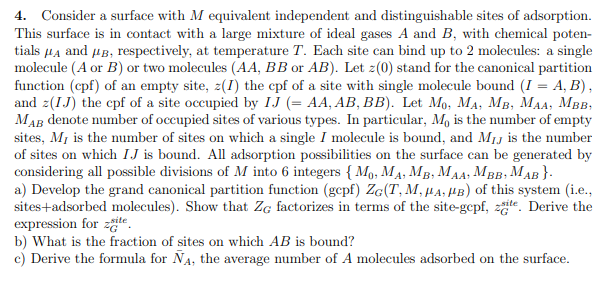
4. Consider a surface with M equivalent independent and distinguishable sites of adsorption. This surface is in contact with a large mixture of ideal gases A and B, with chemical poten- tials MA and B, respectively, at temperature T. Each site can bind up to 2 molecules: a single molecule (A or B) or two molecules (AA, BB or AB). Let z(0) stand for the canonical partition function (cpf) of an empty site, z(1) the cpf of a site with single molecule bound (I = A,B), and z(I.J) the cpf of a site occupied by IJ (= AA, AB, BB). Let Mo, MA, MB, MAA, MBB, MAB denote number of occupied sites of various types. In particular, M, is the number of empty sites, Mi is the number of sites on which a single I molecule is bound, and My is the number of sites on which I J is bound. All adsorption possibilities on the surface can be generated by considering all possible divisions of M into 6 integers { M., MA,MB, MAA: MBB, MAB}. a) Develop the grand canonical partition function (gepf) ZG(T, M, MA,MB) of this system (i.e., sites adsorbed molecules). Show that Zg factorizes in terms of the site-gepf, ate. Derive the expression for zette b) What is the fraction of sites on which AB is bound? c) Derive the formula for NA, the average number of A molecules adsorbed on the surface
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


