Question: 4) (Datapath, Error Detection, 20 points) Implementing LWP instruction: Design a new MIPS instruction 1wp, lood word with pority check: 1wp rt, immCrs) 1wp is
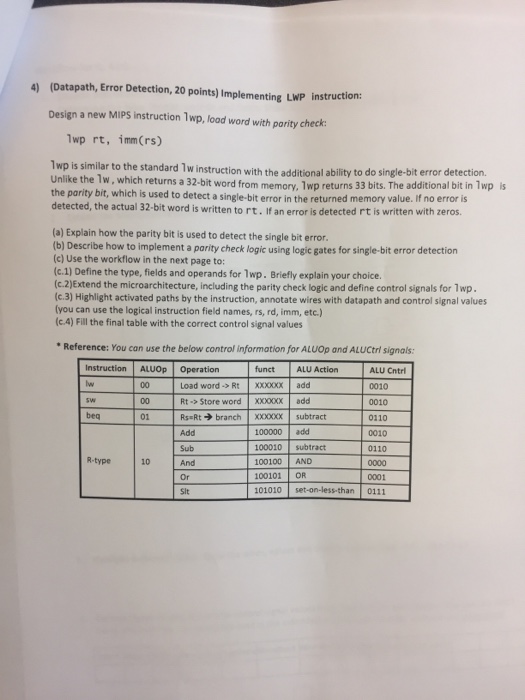
4) (Datapath, Error Detection, 20 points) Implementing LWP instruction: Design a new MIPS instruction 1wp, lood word with pority check: 1wp rt, immCrs) 1wp is similar to the standard 1w instruction with the additiona Unlike the 1w, which returns a 32-bit word from memory, 1wp returns 33 bits. T the parity bit, which is used to detect a single-bit error in the returned memory detected, the actual 32-bit word is written to rt. If an error is I ability to do single-bit error detection. he additional bit in 1wp value. If no error is is detected rt is written with zeros. (a) Explain how the parity bit is used to detect the single bit error. (b) Describe how to implement a parity check logic using logic gates for single-bit error detection (c) Use the workflow in the next page to: (c.1) Define the type, fields and operands for 1wp. Briefly explain your choice (c.2)Extend the microarchitecture, including the parity check logic and define control signals for 1wp. (c3) Highlight activated paths by the instruction, annotate wires with datapath and control signal values (you can use the logical instruction field names, rs, rd, imm, etc.) (c.4) Fill the final table with the correct control signal values Reference: You can use the below control information for ALUOp and ALUCtri signals ALU Cntrl 0010 0010 0110 0010 0110 Instruction ALUOp Operation funct ALU Action Load word->Rtxxxoxxadd Rt Store word XXXOx add RssRt? branch XXXXXX | subtract Add 01 100000add 100010subtract 100100 AND 100101 OR 101010 set-on-lessthan 0111 R-type 10 And Or Sit 0001 4) (Datapath, Error Detection, 20 points) Implementing LWP instruction: Design a new MIPS instruction 1wp, lood word with pority check: 1wp rt, immCrs) 1wp is similar to the standard 1w instruction with the additiona Unlike the 1w, which returns a 32-bit word from memory, 1wp returns 33 bits. T the parity bit, which is used to detect a single-bit error in the returned memory detected, the actual 32-bit word is written to rt. If an error is I ability to do single-bit error detection. he additional bit in 1wp value. If no error is is detected rt is written with zeros. (a) Explain how the parity bit is used to detect the single bit error. (b) Describe how to implement a parity check logic using logic gates for single-bit error detection (c) Use the workflow in the next page to: (c.1) Define the type, fields and operands for 1wp. Briefly explain your choice (c.2)Extend the microarchitecture, including the parity check logic and define control signals for 1wp. (c3) Highlight activated paths by the instruction, annotate wires with datapath and control signal values (you can use the logical instruction field names, rs, rd, imm, etc.) (c.4) Fill the final table with the correct control signal values Reference: You can use the below control information for ALUOp and ALUCtri signals ALU Cntrl 0010 0010 0110 0010 0110 Instruction ALUOp Operation funct ALU Action Load word->Rtxxxoxxadd Rt Store word XXXOx add RssRt? branch XXXXXX | subtract Add 01 100000add 100010subtract 100100 AND 100101 OR 101010 set-on-lessthan 0111 R-type 10 And Or Sit 0001
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


