Question: 4. Given the following empty-stack PDA, (15 points; 8 points for the first 8 blanks) A, Y pop Stavt push(d) pop the language L accepted
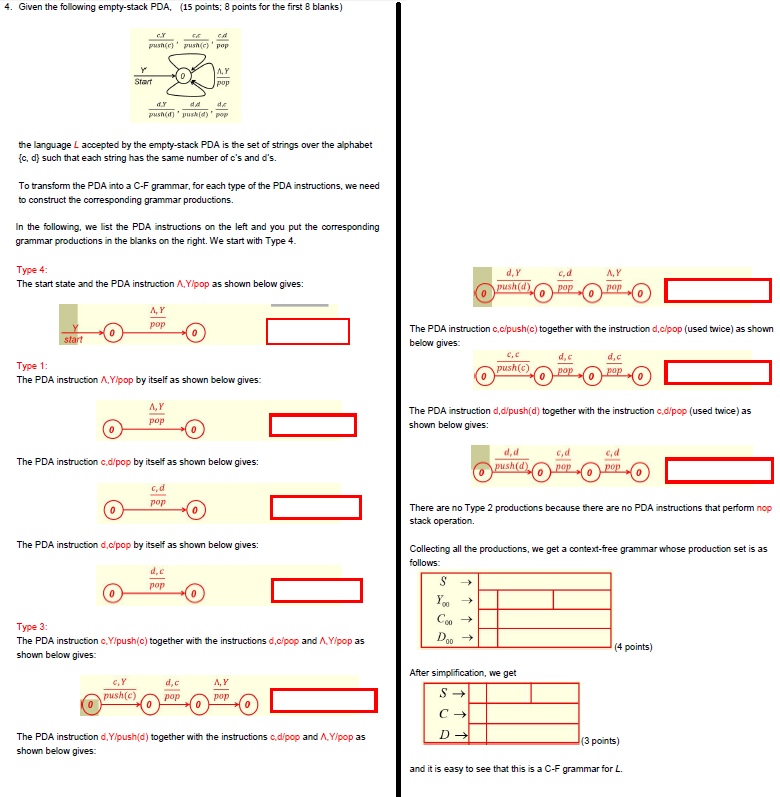
4. Given the following empty-stack PDA, (15 points; 8 points for the first 8 blanks) A, Y pop Stavt push(d) pop the language L accepted by the empty-stack PDA is the set of strings over the alphabet c, d such that each string has the same number of c's and d's. To transform the PDA into a C-F grammar, for each type of the PDA instructions, we need to construct the corresponding grammar productions. In the following, we ist the PDA instructions on the left and you put the corresponding grammar productions in the blanks on the right. We start with Type 4 Type 4 The start state and the PDA instruction AYpop as shown below gives: d, Y A, pop The PDA instruction c,c/push(c) together with the instruction d,clpop (used twice) as shown below gives: Type 1 The PDA instruction A,Ylpop by itself as shown below gives: push(c) A, Y The PDA instruction d,d/push(d) together with the instruction c,d/pop (used twice) as shown below gives: d, d The PDA instruction c,d/pop by itself as shown below gives: pop There are no Type 2 productions because there are no PDA instructions that perform nop stack operation. The PDA instruction d,cpop by itself as shown below gives: Collecting all the productions, we get a context-free grammar whose production set is as Type 3: The PDA instruction cYpush(c) together with the instructions d.cipop and A,Y/pop as shown below gives: (4 points) After simplification, we get push(c) pop The PDA instruction dYpush(d) together with the instructions cdipop and .Yipop as shown below gives: (3 points) t is easy to see that this is a C-F grammar for L 4. Given the following empty-stack PDA, (15 points; 8 points for the first 8 blanks) A, Y pop Stavt push(d) pop the language L accepted by the empty-stack PDA is the set of strings over the alphabet c, d such that each string has the same number of c's and d's. To transform the PDA into a C-F grammar, for each type of the PDA instructions, we need to construct the corresponding grammar productions. In the following, we ist the PDA instructions on the left and you put the corresponding grammar productions in the blanks on the right. We start with Type 4 Type 4 The start state and the PDA instruction AYpop as shown below gives: d, Y A, pop The PDA instruction c,c/push(c) together with the instruction d,clpop (used twice) as shown below gives: Type 1 The PDA instruction A,Ylpop by itself as shown below gives: push(c) A, Y The PDA instruction d,d/push(d) together with the instruction c,d/pop (used twice) as shown below gives: d, d The PDA instruction c,d/pop by itself as shown below gives: pop There are no Type 2 productions because there are no PDA instructions that perform nop stack operation. The PDA instruction d,cpop by itself as shown below gives: Collecting all the productions, we get a context-free grammar whose production set is as Type 3: The PDA instruction cYpush(c) together with the instructions d.cipop and A,Y/pop as shown below gives: (4 points) After simplification, we get push(c) pop The PDA instruction dYpush(d) together with the instructions cdipop and .Yipop as shown below gives: (3 points) t is easy to see that this is a C-F grammar for L
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


