Question: 4 Vertical Alignment Design A road must be designed to cross some railway tracks. The approaches are both flat, with no horizontal curvature and are
Vertical Alignment Design
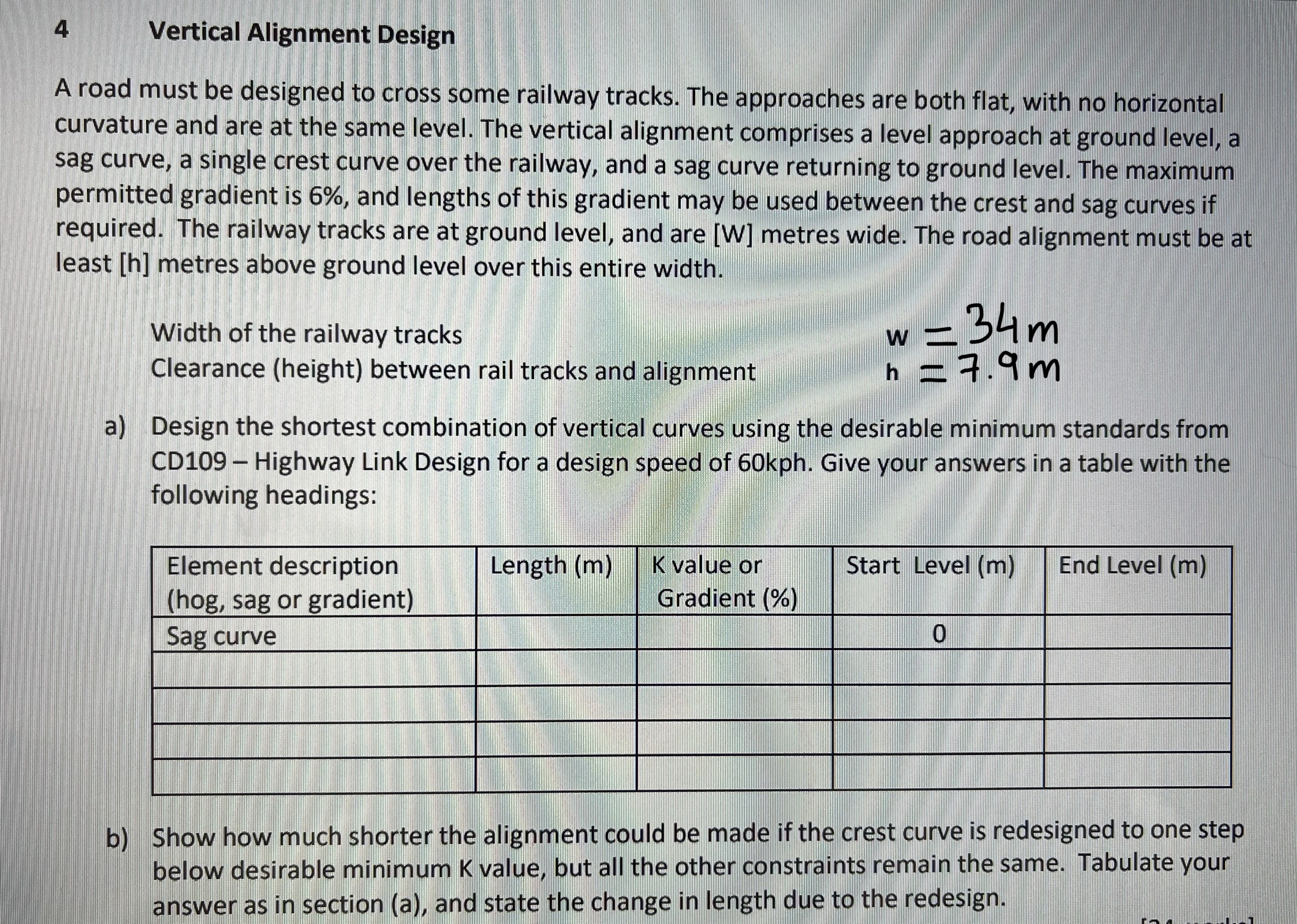
A road must be designed to cross some railway tracks. The approaches are both flat, with no horizontal curvature and are at the same level. The vertical alignment comprises a level approach at ground level, a sag curve, a single crest curve over the railway, and a sag curve returning to ground level. The maximum permitted gradient is and lengths of this gradient may be used between the crest and sag curves if required. The railway tracks are at ground level, and are metres wide. The road alignment must be at least h metres above ground level over this entire width.
Width of the railway tracks
Clearance height between rail tracks and alignment
a Design the shortest combination of vertical curves using the desirable minimum standards from CD Highway Link Design for a design speed of kph Give your answers in a table with the following headings:
tabletableElement descriptionhog sag or gradientLength mtableK value orGradient Start Level End Level mSag curve,,,
b Show how much shorter the alignment could be made if the crest curve is redesigned to one step below desirable minimum value, but all the other constraints remain the same. Tabulate your answer as in section a and state the change in length due to the redesign.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


