Question: 5. Consider a block cipher where the block size is one byte and the encryption (and decryption) algorithm is XORing the plaintext block with a
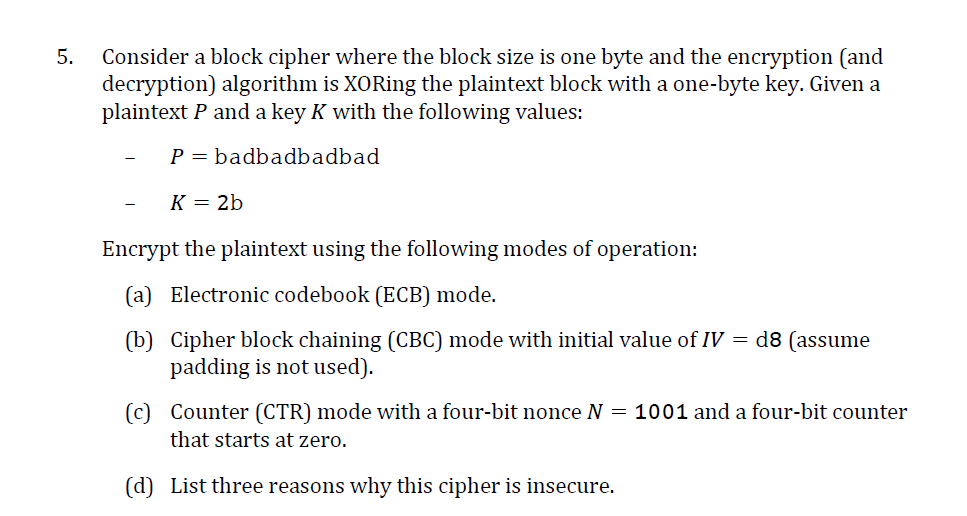
5. Consider a block cipher where the block size is one byte and the encryption (and decryption) algorithm is XORing the plaintext block with a one-byte key. Given a plaintext P and a key K with the following values: P= badbadbadbad K = 2b Encrypt the plaintext using the following modes of operation: (a) Electronic codebook (ECB) mode. (b) Cipher block chaining (CBC) mode with initial value of IV = d8 (assume padding is not used). (C) Counter (CTR) mode with a four-bit nonce N = 1001 and a four-bit counter that starts at zero. (d) List three reasons why this cipher is insecure. 5. Consider a block cipher where the block size is one byte and the encryption (and decryption) algorithm is XORing the plaintext block with a one-byte key. Given a plaintext P and a key K with the following values: P= badbadbadbad K = 2b Encrypt the plaintext using the following modes of operation: (a) Electronic codebook (ECB) mode. (b) Cipher block chaining (CBC) mode with initial value of IV = d8 (assume padding is not used). (C) Counter (CTR) mode with a four-bit nonce N = 1001 and a four-bit counter that starts at zero. (d) List three reasons why this cipher is insecure
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


