Question: 5. Consider a system distributed over its accessible states s in accordance with an arbitrary probability distribution Ps, and let its entropy be defined
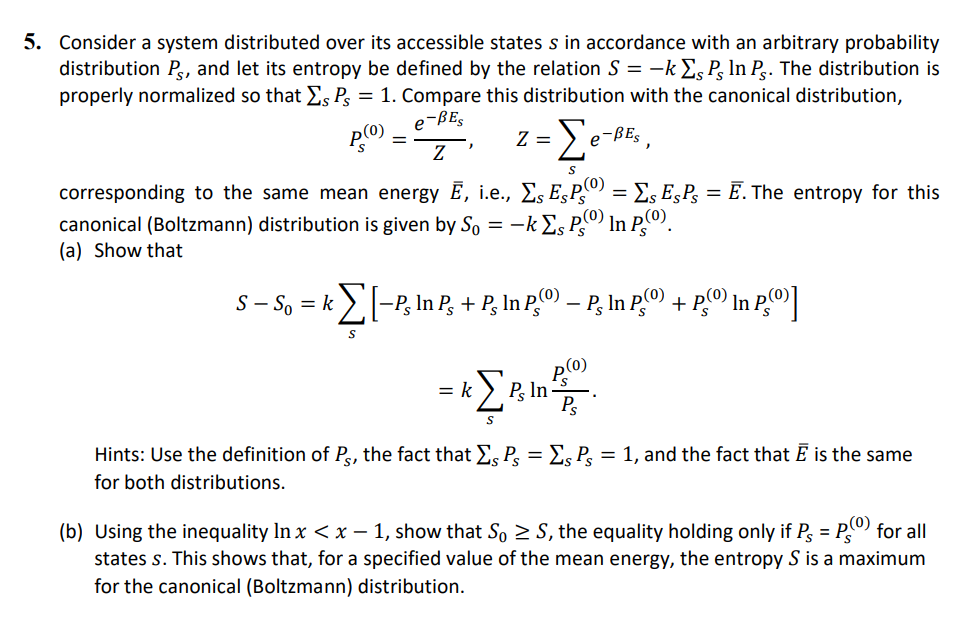
5. Consider a system distributed over its accessible states s in accordance with an arbitrary probability distribution Ps, and let its entropy be defined by the relation S = -k s Ps In Ps. The distribution is properly normalized so that s Ps = 1. Compare this distribution with the canonical distribution, P(0) = e-BES Z = e-BES S corresponding to the same mean energy , i.e., s EP(0) = s EsPs = . The entropy for this canonical (Boltzmann) distribution is given by S = k s P) In P(). (a) Show that S - S = k [-P In P + P In P() P In P + P In P] S = k Ps In Po P(0) Ps Hints: Use the definition of Ps, the fact that s Ps = s Ps = 1, and the fact that is the same for both distributions. (b) Using the inequality In x < x 1, show that So S, the equality holding only if Ps = P(0) for all states s. This shows that, for a specified value of the mean energy, the entropy S is a maximum for the canonical (Boltzmann) distribution.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


