Question: 7. Answer these questions: a. Explains what happens when the DSSS PN sequence at the receiver is not perfectly synchronized with the transmitter's PN sequence.
7. Answer these questions:
a. Explains what happens when the DSSS PN sequence at the receiver is not perfectly synchronized with the transmitter's PN sequence.
b. The signal power passed by a bandpass filter is proportional with the ratio (bandwidth signal passed)/ (bandwidth entire signal). Show why the DSSS gain in SNR is T/T_c, as in the equation below, where 1/T is the data rate, and 1/T_c is the PN signal rate (chip rate).
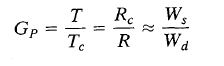
c. The cross correlation between two sources is defined by the equation below. The cross correlation between an m-sequence and noise is low and this is useful to filter noise (advantage 1). This is true in general for DSSS, regardless how the PN is generated. Explain why low cross correlation helps filter out noise.
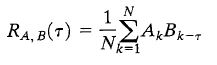
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


