Question: 7. Consider the standard principal-agent model. Agent's utility is given by u(w,e) = 2/w - where w is his wage and e is the level

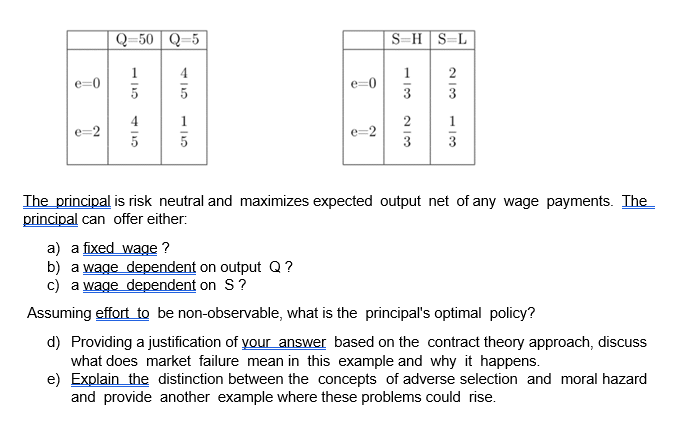
7. Consider the standard principal-agent model. Agent's utility is given by u(w,e) = 2/w - where w is his wage and e is the level of effort. Effort can take two values: e = 0 and e = 2. Agent's reservation utility is 3. Output Q depends on effort and other random factors. Finally, assume the situation where the principal can observe another variable, signal S, whose realization depends on effort as well. It takes two values, S = H for high skill and S = L for low skill. For output Q and signal S we have the following tables of probabilities: Q-50 Q-5 SEH SEL e=0 1 5 e=0 COIN 4 5 e=2 1 3 5 COIN The principal is risk neutral and maximizes expected output net of any wage payments. The principal can offer either: a) a fixed wage ? b) a wage dependent on output Q? c) a wage dependent on S? Assuming effort to be non-observable, what is the principal's optimal policy? d) Providing a justification of your answer based on the contract theory approach, discuss what does market failure mean in this example and why it happens. e) Explain the distinction between the concepts of adverse selection and moral hazard and provide another example where these problems could rise. 7. Consider the standard principal-agent model. Agent's utility is given by u(w,e) = 2/w - where w is his wage and e is the level of effort. Effort can take two values: e = 0 and e = 2. Agent's reservation utility is 3. Output Q depends on effort and other random factors. Finally, assume the situation where the principal can observe another variable, signal S, whose realization depends on effort as well. It takes two values, S = H for high skill and S = L for low skill. For output Q and signal S we have the following tables of probabilities: Q-50 Q-5 SEH SEL e=0 1 5 e=0 COIN 4 5 e=2 1 3 5 COIN The principal is risk neutral and maximizes expected output net of any wage payments. The principal can offer either: a) a fixed wage ? b) a wage dependent on output Q? c) a wage dependent on S? Assuming effort to be non-observable, what is the principal's optimal policy? d) Providing a justification of your answer based on the contract theory approach, discuss what does market failure mean in this example and why it happens. e) Explain the distinction between the concepts of adverse selection and moral hazard and provide another example where these problems could rise
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


