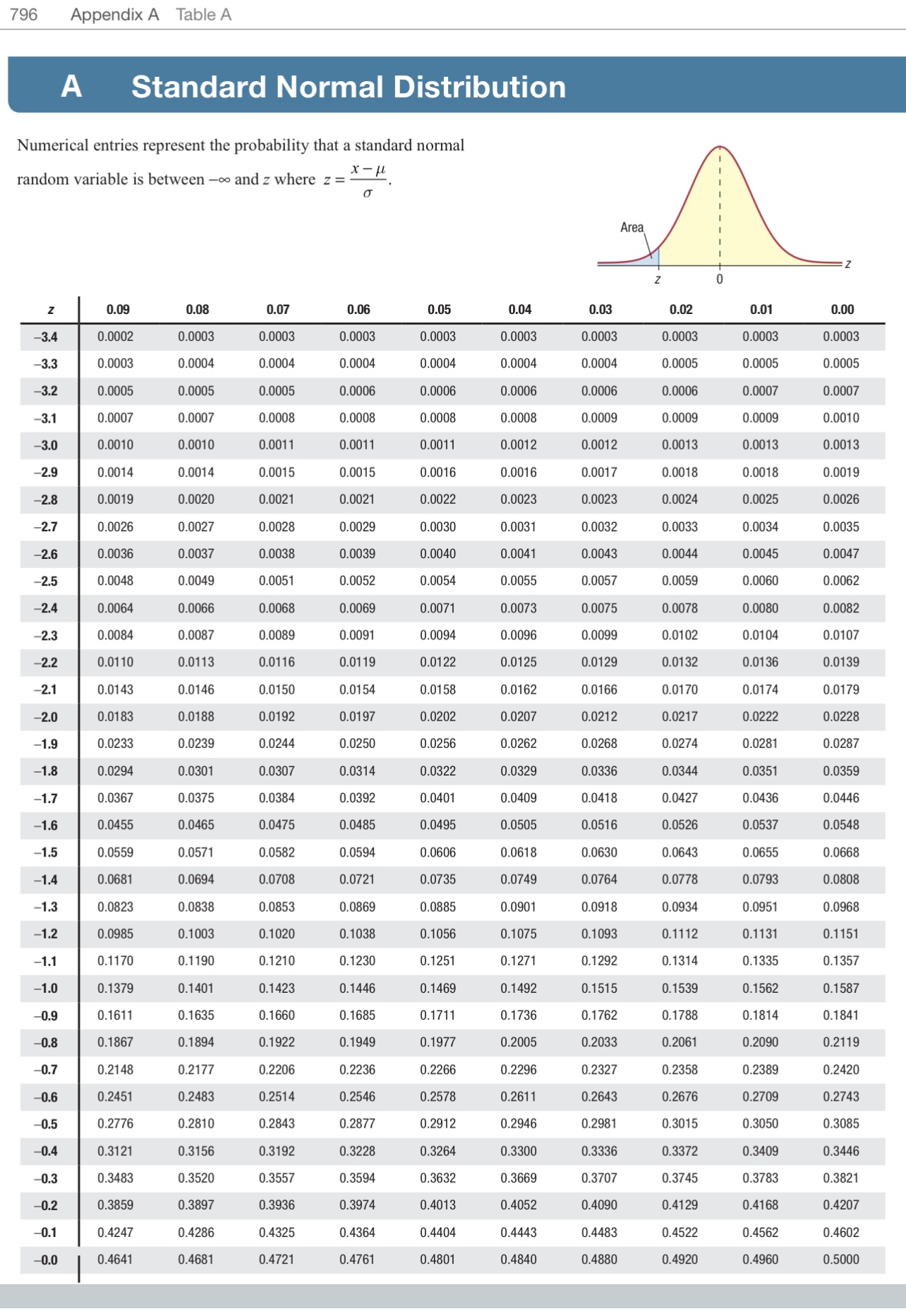
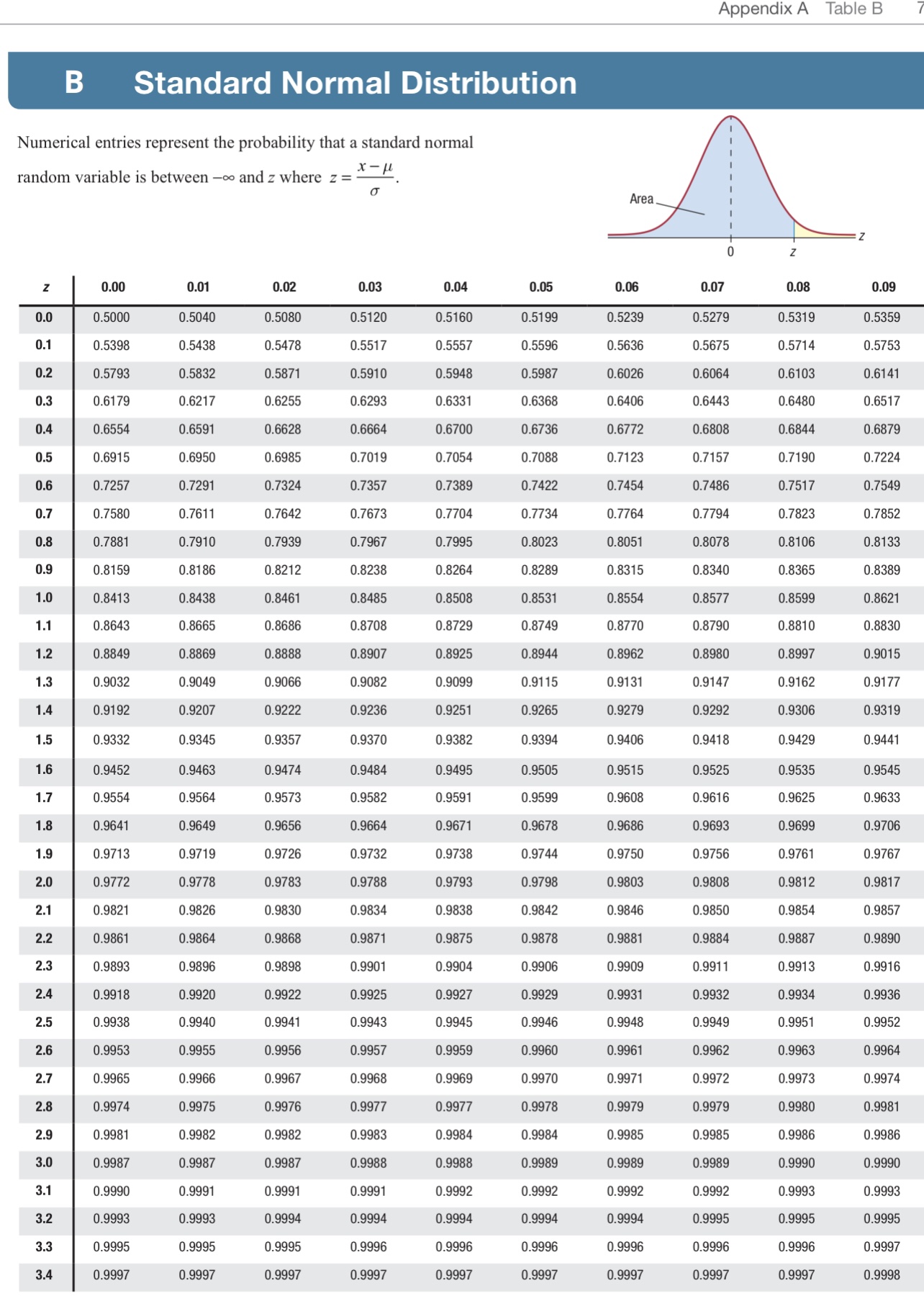
Question: 796 Appendix A Table A A Standard Normal Distribution Numerical entries represent the probability that a standard normal I random variable is between oo and



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


