Question: 8. Set up, but do not evaluate, the double integral of z = f(r, y) over the region R in the ry-plane that computes the

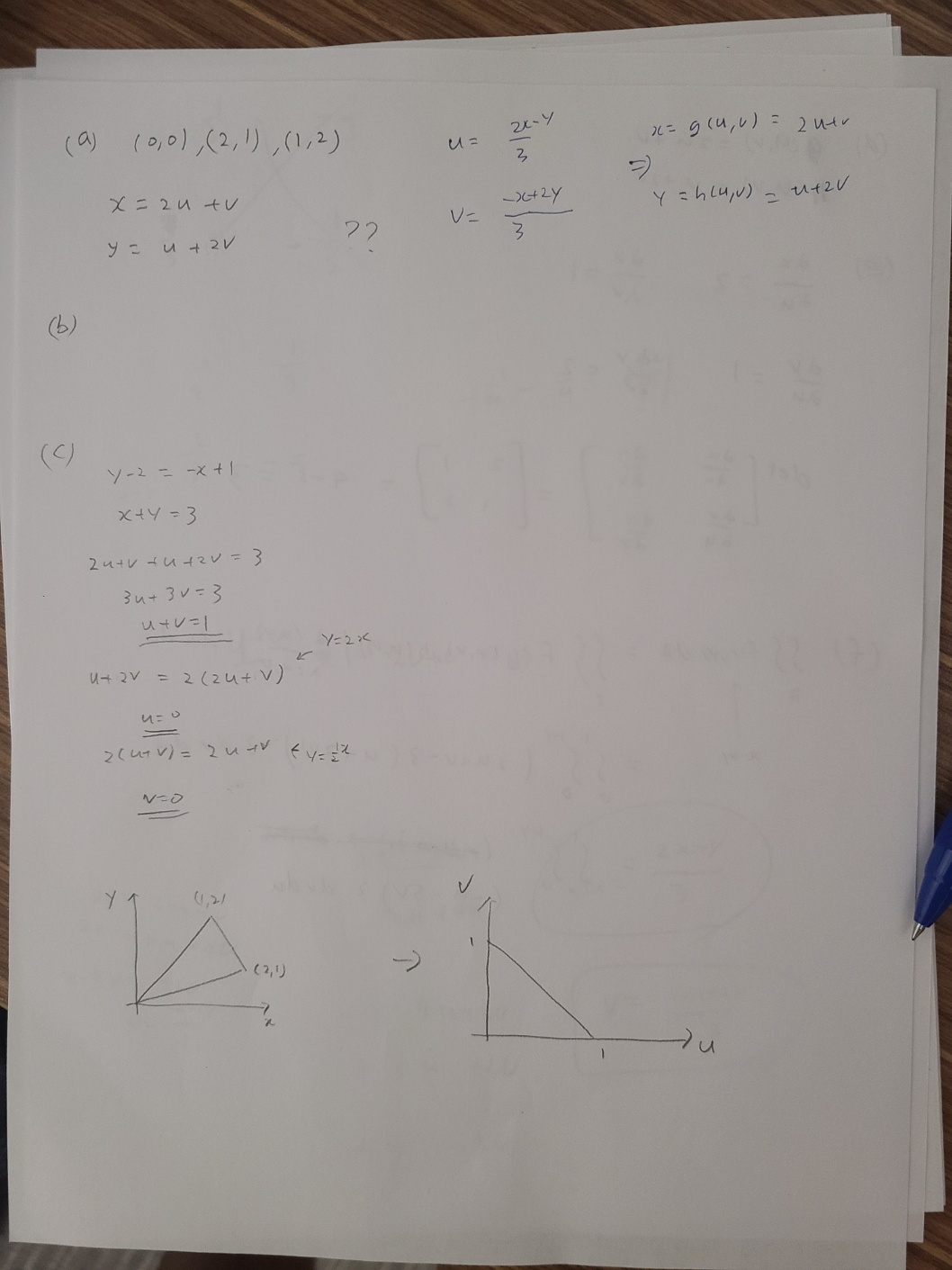
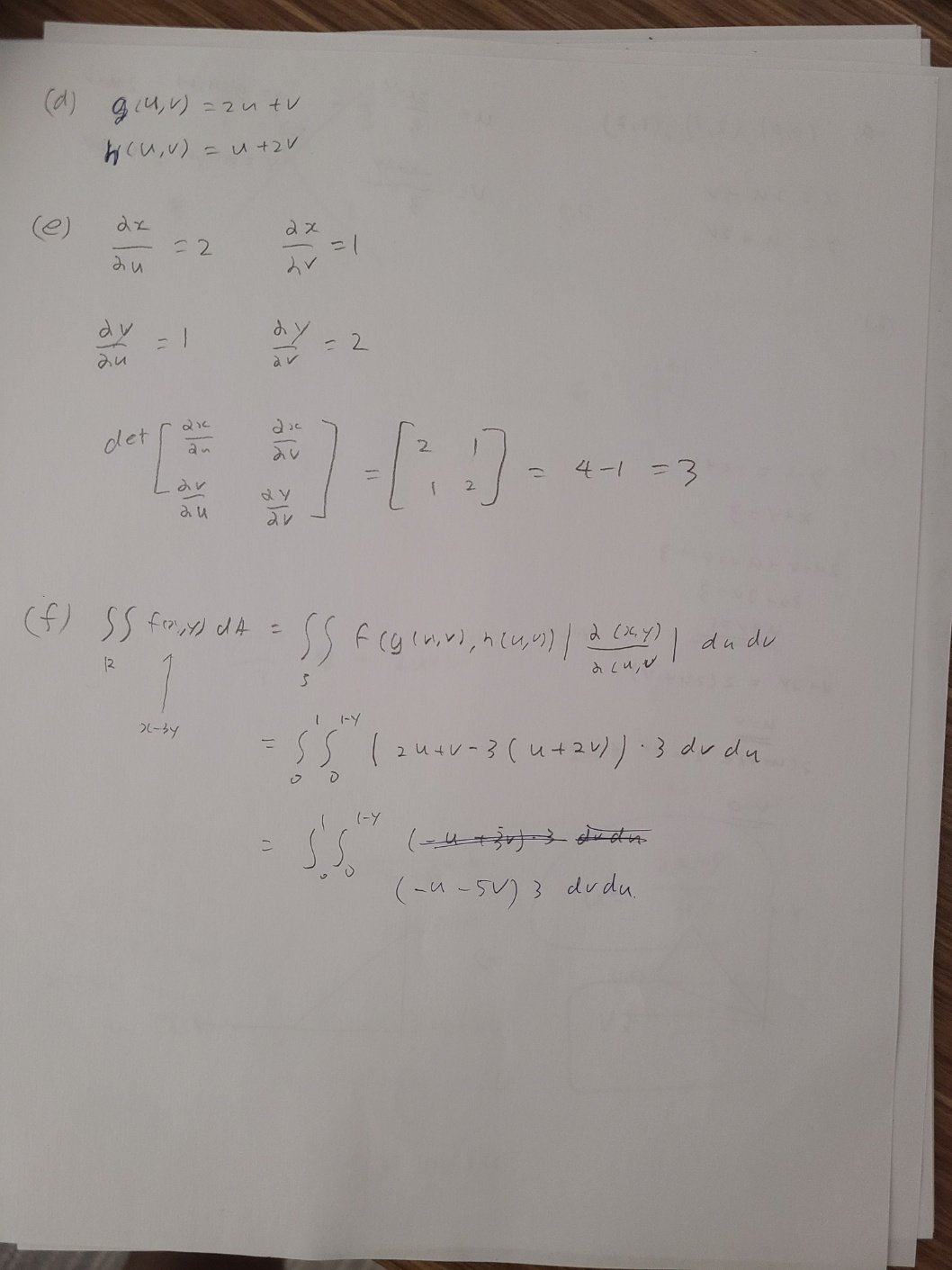

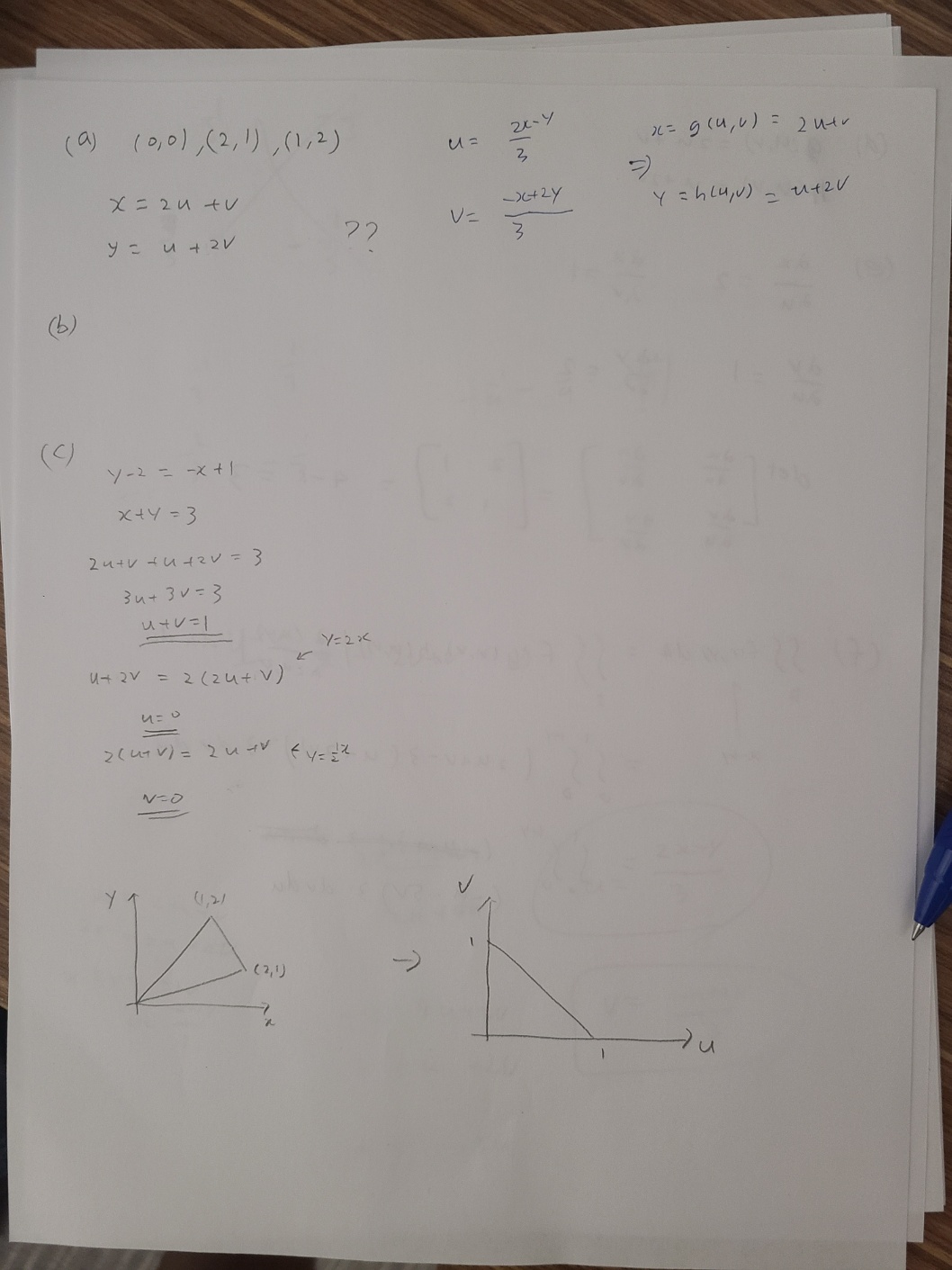
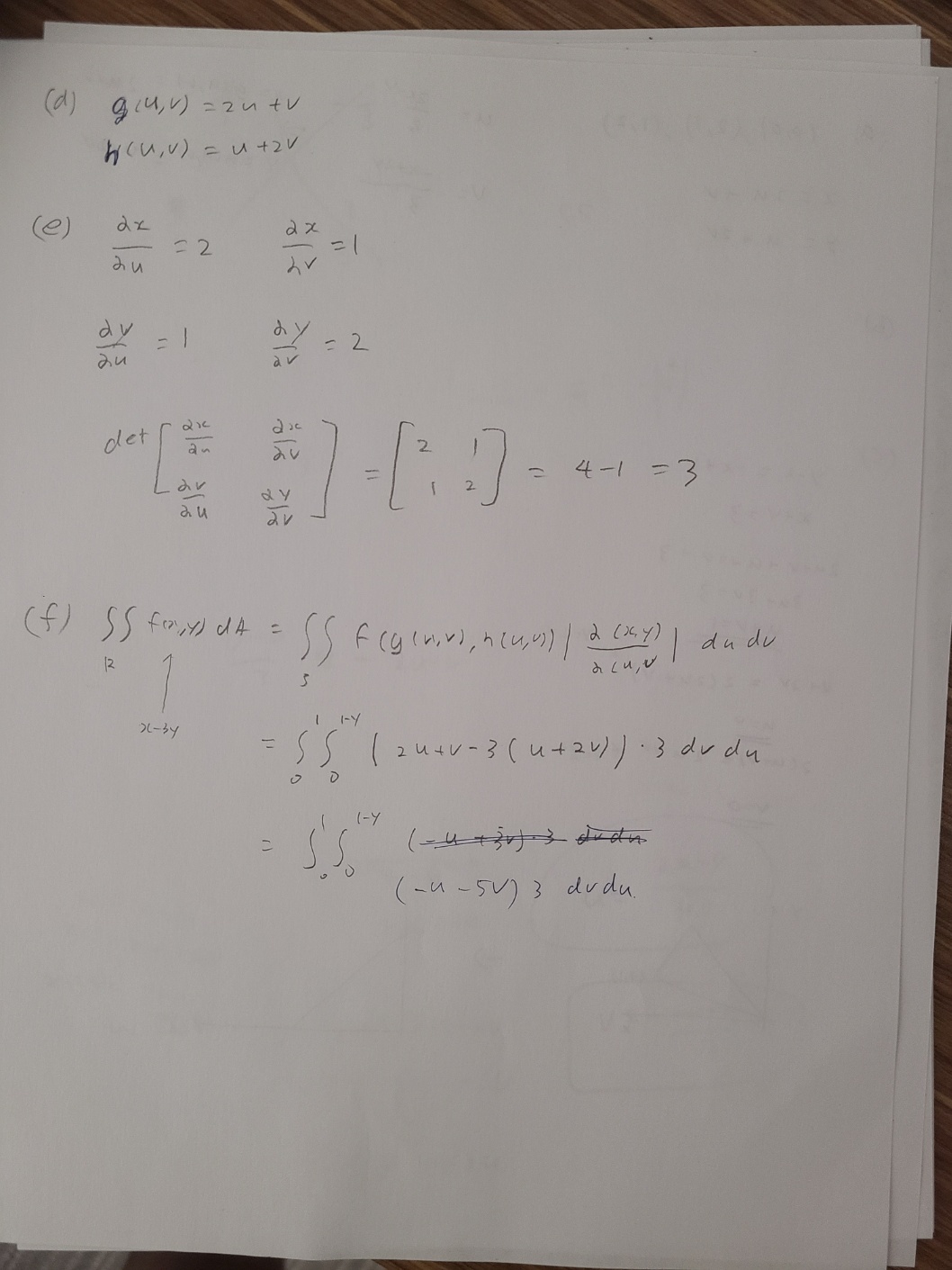
8. Set up, but do not evaluate, the double integral of z = f(r, y) over the region R in the ry-plane that computes the volume of the solid S determined by f by responding to questions a.)-f.) z = ry - y over R = the triangular region bounded by the lines y = 2x, y = 51, and y - 2 = -(x -1) Please notice that these lines intersect at the points (0, 0), (2, 1) and (1, 2). a.) Given R in the problem, find the region S in the uv-plane by finding the transformation T-1 : R - S. Recall that the data of the transformation T-1 is a pair of functions G and H such that u = G(x, y) and v = H(x, y). In practical terms, this means solving for a and y along the boundary of the region R. b.) Justify your solution from a.) by identifying what components of the boundary of S correspond under T-1 to the components of the boundary of R. c.) Sketch the region in the uv-plane. Identify it as a type I or type II region with the notation S = {(u, v)|conditions} d.) Find the transformation T : S - R by determining a pair of functions g and h such that x = g(u, v) and y = h(u, v). In practical terms, this means solving for a and y as functions of u and v by using the G and H you found in part a.) e.) Compute the Jacobian of the transformation you computed in part d.). That is, compute the determinant of the following 2X2 matrix of partial derivatives, viz. Or Or du du det au du denoted below a(x, y) 8(u, v) f.) Set up, but do not evaluation, the double integral of f over the region S. Recall, the theorem states( a) 10, 0) , ( 2 , 1 ) , ( 1 , 2 ) U = * = g ( 4 , " ) = 2 utv 3 X = 24 + V V = 4 = h lu, v ) - utzv y = u + 2V (b ) ( C ) Y - 2 = - * +1 X+4 = 3 2 utv - Utzv = 3 3 u + 3 v = 3 utv= 1 y= 2x u+ 2V= 2 ( 2 4+ V) 2 ( UTV ) = 2 4+V ky= 32 y (1 , 21 V ( 2 , 1 ) I u(d ) glu, v ) = zu tv h (U, V ) = u + 2 V ( e ) = 2 au bv = 1 = 1 = 2 det dy 4-1 = 3 2 v 12 dudu acu,V 21 - 34 1- Y 2 U + V - 3 ( u + 2v ) ) . 3 du du ( - 4 +30 ( - u - 5V) 3 dudu
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


