Question: 9. Consider the following clingo program for lifting problem. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 $ sort and object declarations boolean(t;f). end(leftEnd;rightEnd). height (low;
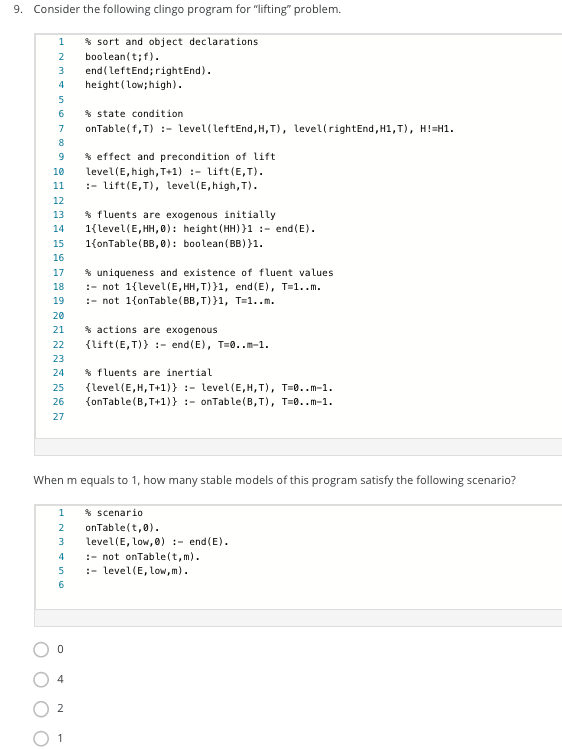
9. Consider the following clingo program for "lifting problem. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 $ sort and object declarations boolean(t;f). end(leftEnd;rightEnd). height (low; high). 9 % state condition onTable(f,T) :- level(leftEnd, H,T), level(rightEnd, H1,T), H!=hl. * effect and precondition of lift level(E, high, T+1) :- lift(E,T). :- lift(e,t), levelle, high, T). 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 % fluents are exogenous initially 1{level (E, HH,0): height (HH)}1 :- end(E). 1{ontable(BB,): boolean (BB)}1. % uniqueness and existence of fluent values :- not l{level(E, HH,T)}1, end(E), T=1..m. :- not 1{ontable(BB,T)}1, T=1..m. 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 $actions are exogenous {lift(E,T)} :- end(E), T=o..m-1. % fluents are inertial {level(E,H,T+1)} :- level(E,H,T), T=8..m-1. {ontable(B.T+1)} :-onTable(B,T), T=8..m-1. When m equals to 1, how many stable models of this program satisfy the following scenario? 1 2 3 4 5 6 % scenario onTable(t,0). level(E, low,o) :- end(E). :- not onTablelt,m). :- level(E, low,m). 0 4 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


