Question: 9-22 Absorption versus variable costing. Electron Inc. is a semiconductor company based in Winnipeg. In 2018, it produced a new router system for its corporate
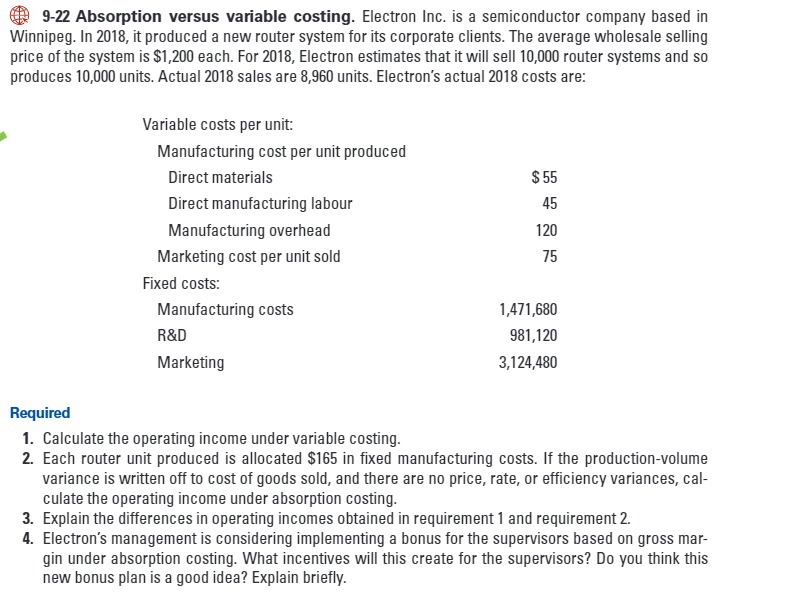
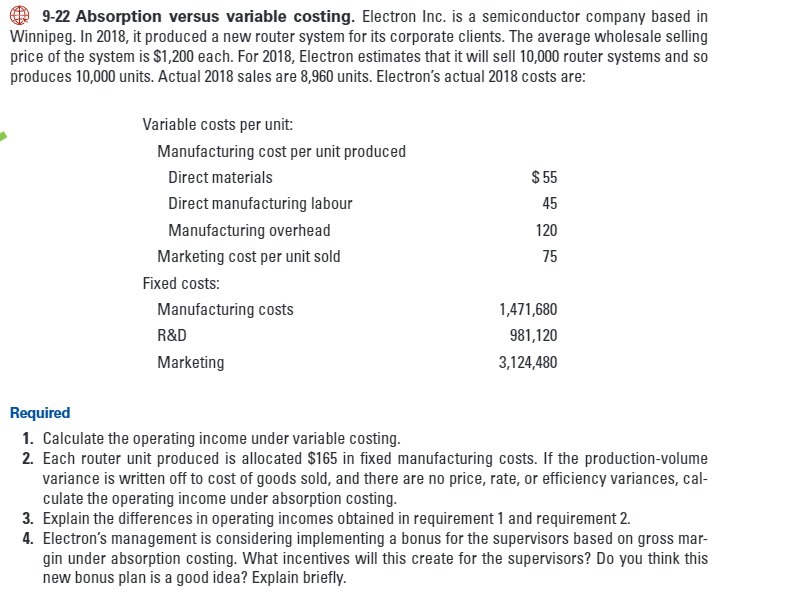
9-22 Absorption versus variable costing. Electron Inc. is a semiconductor company based in Winnipeg. In 2018, it produced a new router system for its corporate clients. The average wholesale selling price of the system is $1,200 each. For 2018, Electron estimates that it will sell 10,000 router systems and so produces 10,000 units. Actual 2018 sales are 8,960 units. Electron's actual 2018 costs are: Variable costs per unit: Manufacturing cost per unit produced Direct materials $ 55 Direct manufacturing labour 45 Manufacturing overhead 120 Marketing cost per unit sold 75 Fixed costs: Manufacturing costs 1,471,680 R&D 981,120 Marketing 3,124,480 Required 1. Calculate the operating income under variable costing. 2. Each router unit produced is allocated $165 in fixed manufacturing costs. If the production-volume variance is written off to cost of goods sold, and there are no price, rate, or efficiency variances, cal- culate the operating income under absorption costing 3. Explain the differences in operating incomes obtained in requirement 1 and requirement 2. 4. Electron's management is considering implementing a bonus for the supervisors based on gross mar- gin under absorption costing. What incentives will this create for the supervisors? Do you think this new bonus plan is a good idea? Explain briefly
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


