Question: a (a) For what conditions is the Leveque approximation valid? (b) For the Leveque problem derived in class for a pipe with diameter d and
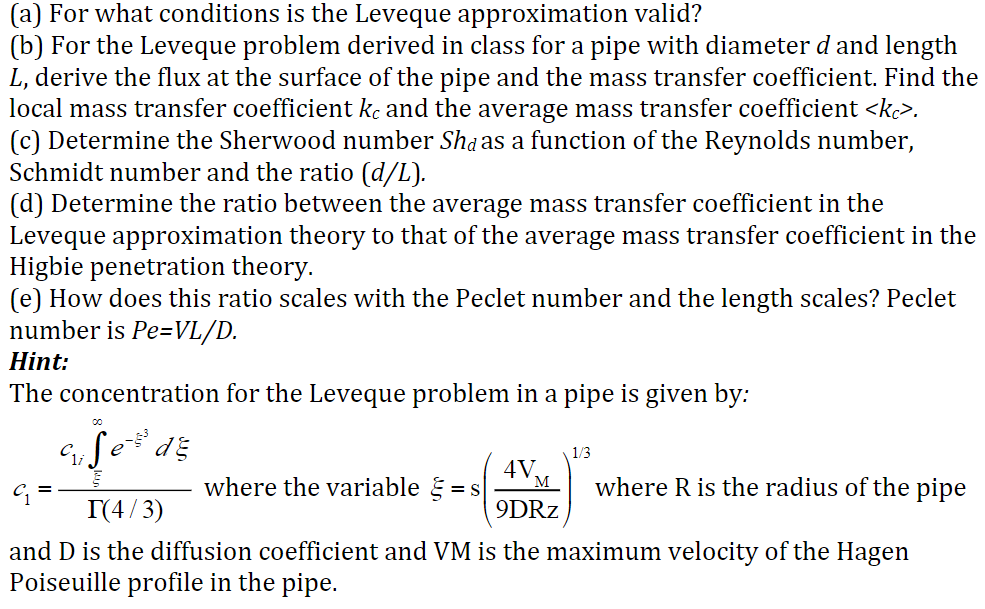
a (a) For what conditions is the Leveque approximation valid? (b) For the Leveque problem derived in class for a pipe with diameter d and length L, derive the flux at the surface of the pipe and the mass transfer coefficient. Find the local mass transfer coefficient kc and the average mass transfer coefficient
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


