Question: A) An adjacency matrix has as many rows and columns as there are nodes. The entries in an adjacency matrix are 0's and 1's. If
A) An adjacency matrix has as many rows and columns as there are nodes. The entries in an adjacency matrix are 0's and 1's. If there is an edge from node N to node M (in other words, if N and M are neighbors), then there is a 1 in row N, column M of the adjacency matrix. Note that in the situation we are considering, an edge from N to M is also an edge from M to N, so there will also be a 1 in row M, column N of the adjacency matrix. (In other words, the adjacency matrix will be symmetric across the main diagonal.)
For example, for this small client-server network:
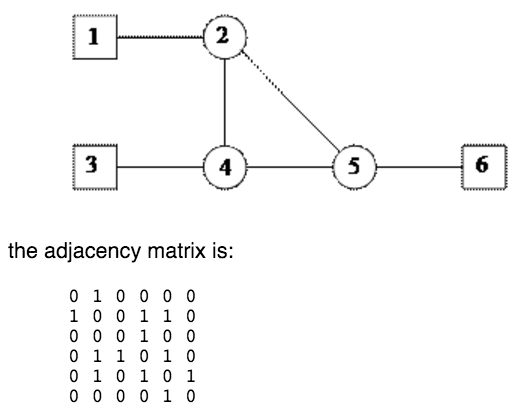
So, from the first row we can see th?at node 1is connected to node 2; the second row indicates that node 2 is connected to nodes 1, 4, and 5; the third row indicates that node 3 is connected to node 2, etc.
B) The solveClientServer function
The solveClientServer function takes one parameter, adjMatrix (an adjacency matrix), solves the linear system for a network of clients and servers represented by the adjacency matrix, and returns the results (i.e., the solution to the linear system) as a column vector. The solveClientServer function should assume that the adjacency matrix is valid.
Recall that the equations for this linear system are
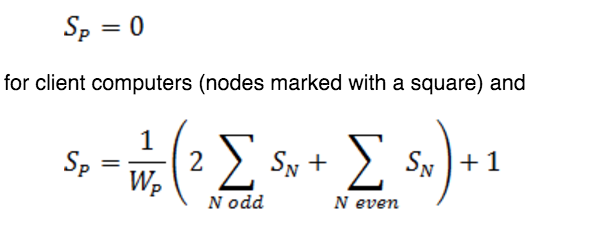
for servers (nodes marked with a circle), where the first sum is over all odd-numbered nodes that are linked to node P, the second sum is over all the even-numbered nodes that are linked to node P, and the value of WP is a weighted sum of the number of nodes that are linked to the node P where odd-numbered nodes have a weight of two and even numbered nodes have a weight of one. WP is called the weight of the node.
Your solveClientServer function must implement the following algorithm to set up and solve this linear system:
Create Nnbrs, a column vector containing the number of neighbors each node has (hint: use the sum command and the adjacency matrix)
Multiply the odd columns of the adjacency matrix by 2 (we'll call the result Mwt)
Calculate the vector of weights, Wp (hint: use the sum command and Mwt)
Set A (the coefficient matrix for the linear system) to be an appropriately-sized identity matrix
Set b (the right-hand side vector for the linear system) to be an appropriately-sized vector containing all ones
for each node N (i.e., for each row of A)
if N has only 1 neighbor (i.e., N is a client computer), then all that needs to be done is to set b(N) to 0
otherwise, N is a server, so we need to set the appropriate spots in the current row of A to the appropriate values.
multiply the corresponding row of Mwt by -1 and divide it by WN (Note that this row of Mwt now has the appropriate coefficients for the nodes other than N in the equation for node N. )
add this row to the current row of A (which already contains the coefficient of 1 for node N)
Solve the linear system
D) The main program
The main program should go in your script and must implement the following algorithm:
ask the user for the name of the adjacency matrix file load the adjacency matrix from the file solve the linear system (using solveClientServer) use a for loop to display the results (in the format shown in the sample runs)
You may assume that the file name entered by the user is the name of a file that does exist. You may also assume that any file you load is a text file containing a valid adjacency matrix.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


