Question: (a) (b) Assuming that the system is having the same annual savings of 2 million year and the MARR is 7%, recommend the best alternative

![best alternative using AIRR analysis. [30 Marks] [CO2, PO2, C4] From the](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f1faec18f1c_44366f1faeb9b120.jpg)
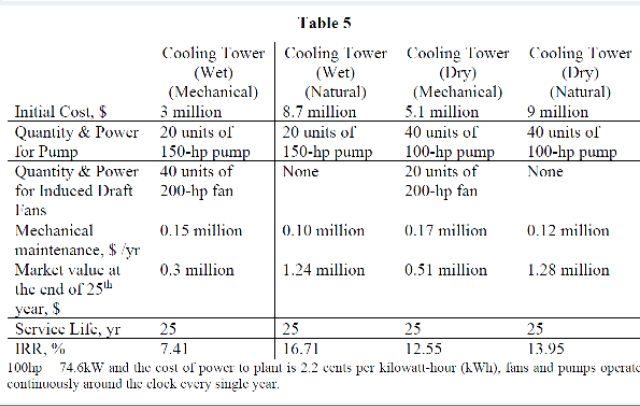
(a) (b) Assuming that the system is having the same annual savings of 2 million year and the MARR is 7%, recommend the best alternative using AIRR analysis. [30 Marks] [CO2, PO2, C4] From the decision made in QUESTION 3 (a), calculate the after-tax rate of return using a 39% income tax rate. For this case, straight line (SI) depreciation applies. Initial Cost, $ Quantity & Power for Pump Quantity & Power for Induced Draft l'ans Mechanical maintenance, $/yr Market value at the end of 25th year, $ Service Life, yr IRR, % Cooling Tower (Wet) (Mechanical) 3 million 20 units of 150-hp pump 40 units of 200-hp fan 0.15 million 0.3 million Table 5 Cooling Tower (Wet) (Natural) 8.7 million 20 units of 150-hp pump None 0.10 million 1.24 million Cooling Tower (Dry) (Mechanical) 5.1 million 40 units of 100-hp pump 20 units of 200-hp fan 0.17 million 0.51 million Cooling Tower (Dry) (Natural) 9 million 40 units of 100-hp pump None 0.12 million 1.28 million 25 25 25 12.55 25 13.95 7.41 16.71 100hp 74.6kW and the cost of power to plant is 2.2 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh), fans and pumps operate continuously around the clock every single year. In a 200 MW of the steam-electric power plant, the utilization of a cooling tower is suggested to cool the condenser effluent and simultaneously dissipate the waste heat into the atmosphere. There are a few types and specifications of cooling towers depending on the cooling methods (i.e. wet or dry) and the movement of air (i.e. mechanical forces or natural draft). Table 5 shows the specification for the colling towers. (a) (b) Assuming that the system is having the same annual savings of 2 million year and the MARR is 7%, recommend the best alternative using AIRR analysis. [30 Marks] [CO2, PO2, C4] From the decision made in QUESTION 3 (a), calculate the after-tax rate of return using a 39% income tax rate. For this case, straight line (SI) depreciation applies. Initial Cost, $ Quantity & Power for Pump Quantity & Power for Induced Draft l'ans Mechanical maintenance, $/yr Market value at the end of 25th year, $ Service Life, yr IRR, % Cooling Tower (Wet) (Mechanical) 3 million 20 units of 150-hp pump 40 units of 200-hp fan 0.15 million 0.3 million Table 5 Cooling Tower (Wet) (Natural) 8.7 million 20 units of 150-hp pump None 0.10 million 1.24 million Cooling Tower (Dry) (Mechanical) 5.1 million 40 units of 100-hp pump 20 units of 200-hp fan 0.17 million 0.51 million Cooling Tower (Dry) (Natural) 9 million 40 units of 100-hp pump None 0.12 million 1.28 million 25 25 25 12.55 25 13.95 7.41 16.71 100hp 74.6kW and the cost of power to plant is 2.2 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh), fans and pumps operate continuously around the clock every single year. In a 200 MW of the steam-electric power plant, the utilization of a cooling tower is suggested to cool the condenser effluent and simultaneously dissipate the waste heat into the atmosphere. There are a few types and specifications of cooling towers depending on the cooling methods (i.e. wet or dry) and the movement of air (i.e. mechanical forces or natural draft). Table 5 shows the specification for the colling towers
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


