Question: A B C D E F G H (sec.) 20 30 25 10 55 30 25 40 A D, B, C E F, G (a)
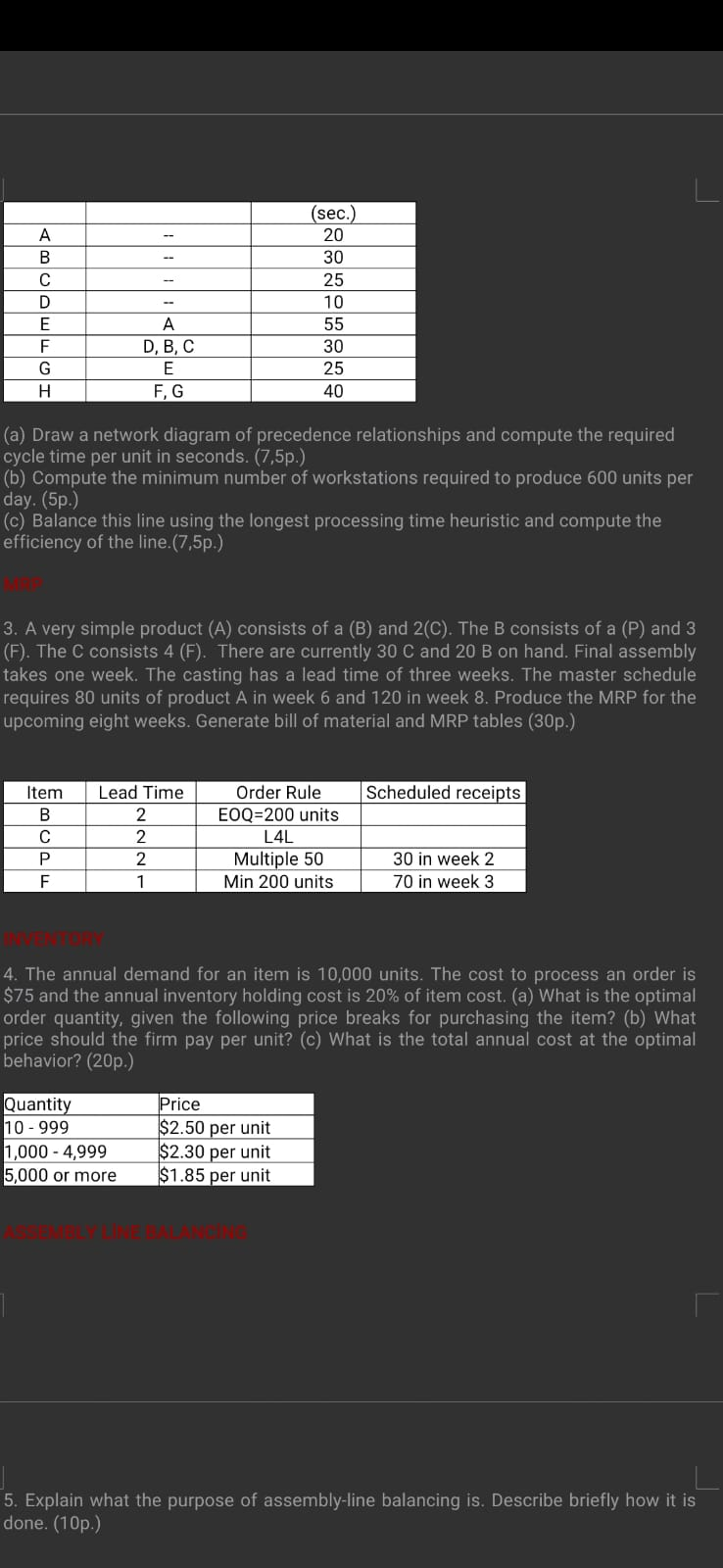
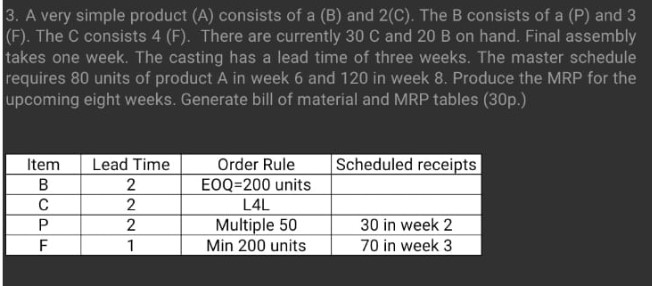

A B C D E F G H (sec.) 20 30 25 10 55 30 25 40 A D, B, C E F, G (a) Draw a network diagram of precedence relationships and compute the required cycle time per unit in seconds. (7,5p.) (b) Compute the minimum number of workstations required to produce 600 units per day. (5p.) (c) Balance this line using the longest processing time heuristic and compute the efficiency of the line.(7,5p.) 3. A very simple product (A) consists of a (B) and 2(C). The B consists of a (P) and 3 (F). The C consists 4 (F). There are currently 30 C and 20 B on hand. Final assembly takes one week. The casting has a lead time of three weeks. The master schedule requires 80 units of product A in week 6 and 120 in week 8. Produce the MRP for the upcoming eight weeks. Generate bill of material and MRP tables (30p.) Scheduled receipts Item B F Lead Time 2 2 2 1 Order Rule EOQ=200 units L4L Multiple 50 Min 200 units 30 in week 2 70 in week 3 4. The annual demand for an item is 10,000 units. The cost to process an order is $75 and the annual inventory holding cost is 20% of item cost. (a) What is the optimal order quantity, given the following price breaks for purchasing the item? (b) What price should the firm pay per unit? (c) What is the total annual cost at the optimal behavior? (20p.) Quantity 10 - 999 1,000 - 4,999 5,000 or more Price $2.50 per unit $2.30 per unit $1.85 per unit 5. Explain what the purpose of assembly-line balancing is. Describe briefly how it is done. (10p.) 3. A very simple product (A) consists of a (B) and 2(C). The B consists of a (P) and 3 (F). The C consists 4 (F). There are currently 30 C and 20 B on hand. Final assembly takes one week. The casting has a lead time of three weeks. The master schedule requires 80 units of product A in week 6 and 120 in week 8. Produce the MRP for the upcoming eight weeks. Generate bill of material and MRP tables (30p.) Lead Time 2 Scheduled receipts Item B P F ANINI Order Rule EOQ=200 units L4L Multiple 50 Min 200 units 30 in week 2 70 in week 3 LMRP 3. A very simple product (CA) consist of 6 (B) and ((c). The B consist of a (P) and 3(F). The c consist 4CF) There are currently 30c and 208 on hand. Finan assembly takes one week. The master schedule requies 80 units of product of product A in weet 6 and 125 in week 8. Produce the MRP for the upcoming eight weeks. Generate bill of material chd MRP tables. (300) AB-266) kad tine 2 2 300 206 order Rule fchedularecies EOQ 200 units cut Multiple so Ron week? Min 20 Qunits 70th week C 2 6. hatta 80 bit A 8. Woulta ho bir A A B C D E F G H (sec.) 20 30 25 10 55 30 25 40 A D, B, C E F, G (a) Draw a network diagram of precedence relationships and compute the required cycle time per unit in seconds. (7,5p.) (b) Compute the minimum number of workstations required to produce 600 units per day. (5p.) (c) Balance this line using the longest processing time heuristic and compute the efficiency of the line.(7,5p.) 3. A very simple product (A) consists of a (B) and 2(C). The B consists of a (P) and 3 (F). The C consists 4 (F). There are currently 30 C and 20 B on hand. Final assembly takes one week. The casting has a lead time of three weeks. The master schedule requires 80 units of product A in week 6 and 120 in week 8. Produce the MRP for the upcoming eight weeks. Generate bill of material and MRP tables (30p.) Scheduled receipts Item B F Lead Time 2 2 2 1 Order Rule EOQ=200 units L4L Multiple 50 Min 200 units 30 in week 2 70 in week 3 4. The annual demand for an item is 10,000 units. The cost to process an order is $75 and the annual inventory holding cost is 20% of item cost. (a) What is the optimal order quantity, given the following price breaks for purchasing the item? (b) What price should the firm pay per unit? (c) What is the total annual cost at the optimal behavior? (20p.) Quantity 10 - 999 1,000 - 4,999 5,000 or more Price $2.50 per unit $2.30 per unit $1.85 per unit 5. Explain what the purpose of assembly-line balancing is. Describe briefly how it is done. (10p.) 3. A very simple product (A) consists of a (B) and 2(C). The B consists of a (P) and 3 (F). The C consists 4 (F). There are currently 30 C and 20 B on hand. Final assembly takes one week. The casting has a lead time of three weeks. The master schedule requires 80 units of product A in week 6 and 120 in week 8. Produce the MRP for the upcoming eight weeks. Generate bill of material and MRP tables (30p.) Lead Time 2 Scheduled receipts Item B P F ANINI Order Rule EOQ=200 units L4L Multiple 50 Min 200 units 30 in week 2 70 in week 3 LMRP 3. A very simple product (CA) consist of 6 (B) and ((c). The B consist of a (P) and 3(F). The c consist 4CF) There are currently 30c and 208 on hand. Finan assembly takes one week. The master schedule requies 80 units of product of product A in weet 6 and 125 in week 8. Produce the MRP for the upcoming eight weeks. Generate bill of material chd MRP tables. (300) AB-266) kad tine 2 2 300 206 order Rule fchedularecies EOQ 200 units cut Multiple so Ron week? Min 20 Qunits 70th week C 2 6. hatta 80 bit A 8. Woulta ho bir A







