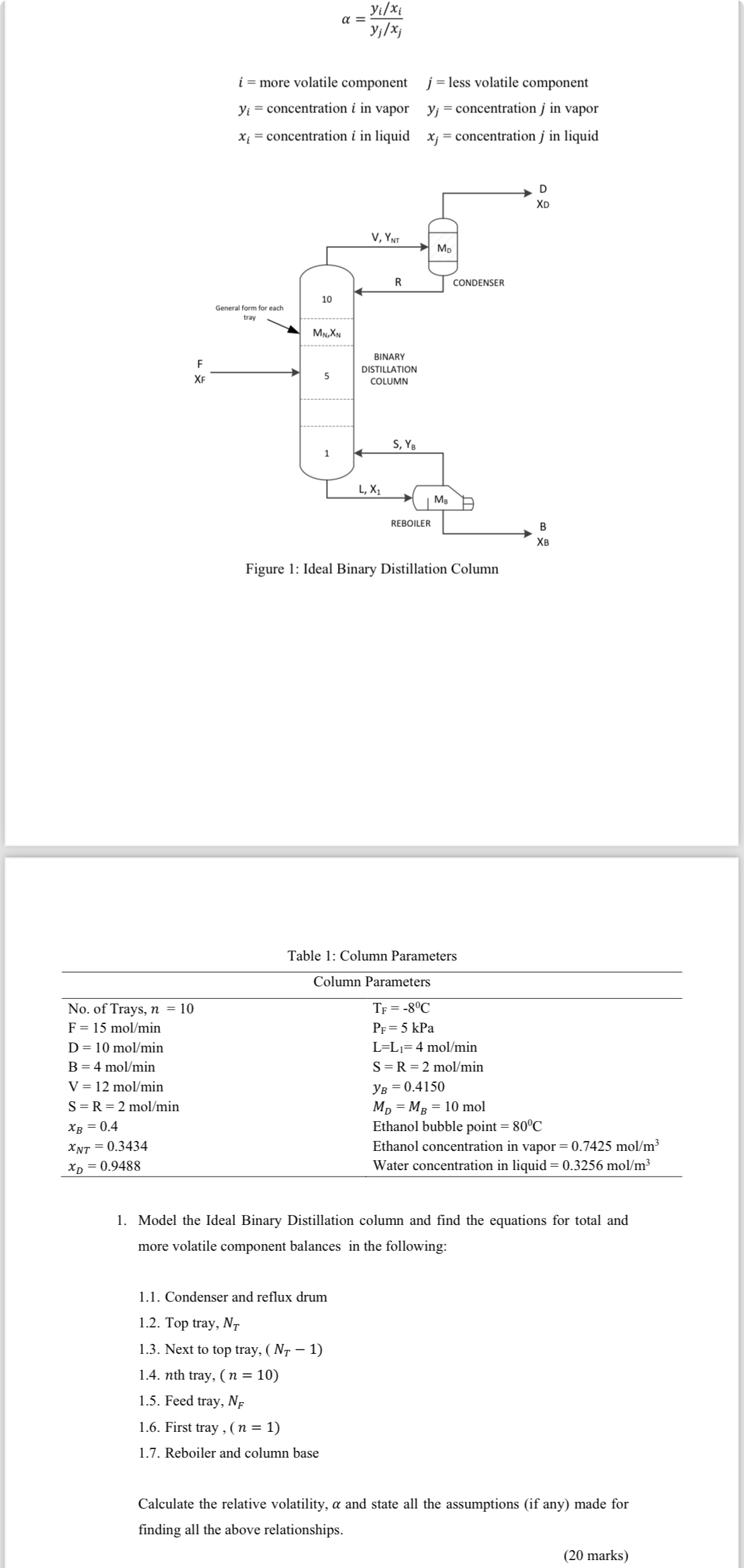
Question: A binary distillation column as in Figure 1 is considered as a case study in this project. Distillation column is used in many chemical processes
A binary distillation column as in Figure is considered as a case study in this project. Distillation column is used in many chemical processes for separating feed streams and purification of final and intermediate product streams. There are trays in the column to separate two components ethanolwater with as the inlet, as the distillate and is the bottom flow rate. The purpose of the control systems is to maintain the top, and bottom product composition, at the desired set points despite variations in the inlet condition and # The overhead vapor is totally condensed in a condenser and flows into the reflux drum, whose holdup of liquid is moles and the drum contents are assumed perfectly mixed. At the base of the column, it is assumed that assume that the liquids in the reboiler are also perfectly mixed with similar composition and total holdup moles The composition of the vapor leaving the base of the column and entering first tray is For column contains a total of trays the composition on each is assumed to be $ with holdup $ moles The details parameters are tabulated in Table Assumptions: It is a binary system involving two components The components are with constant relative volatility throughout the column Delay time in the vapor line, heat losses and temperature changes from trayto tray is negligible Neglect the dynamic of both condenser and reboiler Liquid in the reboiler and in column base are perfectly mixed No chemical reaction occurs in the column The vapor leaving the tray is in equilibrium with liquid on the tray efficiencies Therefore, the simple vaporliquid equilibrium relationship may be used: liquid composition on the th tray mole fraction more volatile component vapor composition on the th tray mole fraction more volatile component relative volatility and is given by: && more volatile component concentration in vapor less volatile component concentration in vapor& concentration in liquid concentration in liquid.Question: Model the Ideal Binary Distillation column and find the equations for total and more volatile component balances in the following: Condenser and reflux drum Top tray, Next to top tray, th tray, Feed tray, # First tray Reboiler and column baseCalculate the relative volatility, and state all the assumptions if any made for finding all the above relationships.
more volatile component less volatile component
concentration in vapor concentration in vapor
concentration in liquid concentration in liquid
Table : Column Parameters
tableColumn Parameters of Trays,
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


