Question: a. Formulate a linear programming model so that DEA approach can be used to evaluate the performance of hospital D. b. Solve the problem formulated
a. Formulate a linear programming model so that DEA approach can be used to evaluate the performance of hospital D.
b. Solve the problem formulated in (a), and show all of the Excel or QM templates you use in your formulation.
c. Is hospital D relatively inefficient? What is your interpretation of the value of the objective function?
d. How many patient-days of each type are produced by the composite hospital?
e. Which hospital would you recommend hospital D consider emulating to improve the efficiency of its operation?
f. Formulate a linear programming model so that DEA approach can be used to evaluate the performance of hospital E.
g. Solve the problem formulated in (f), and show all of the Excel or QM templates you use in your formulation.
h. Is hospital E relatively inefficient? What is your interpretation of the value of the objective function?
i. Give an interpretation of the results (i.e., the sensitivity reports) in terms of all of the inputs and output measures.
j. Based on the results, which hospitals are involved in making up the composite hospital? Can you make up a general statement about which hospitals will make up the composite unit associated with a unit that is not inefficient?
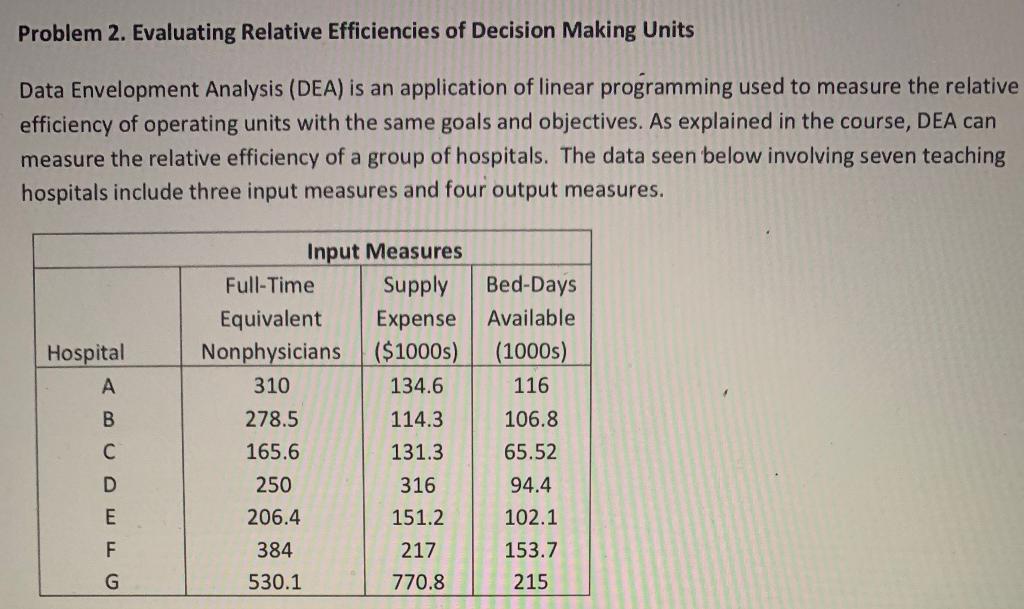
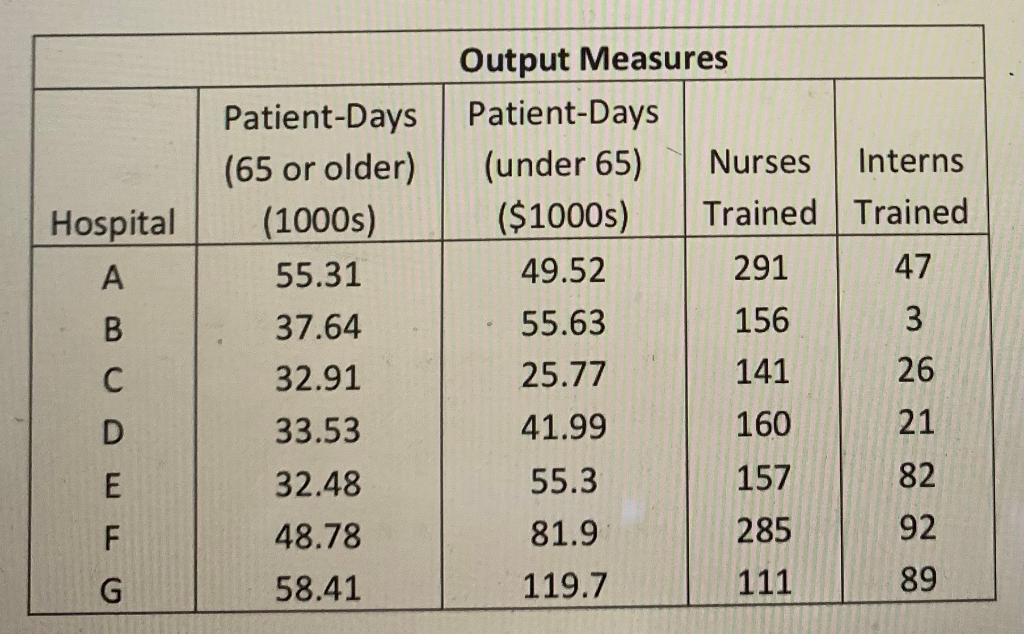
Problem 2. Evaluating Relative Efficiencies of Decision Making Units Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) is an application of linear programming used to measure the relative efficiency of operating units with the same goals and objectives. As explained in the course, DEA can measure the relative efficiency of a group of hospitals. The data seen below involving seven teaching hospitals include three input measures and four output measures. Bed-Days Available (1000s) 116 Hospital B Input Measures Full-Time Supply Equivalent Expense Nonphysicians ($1000s) 310 134.6 278.5 114.3 165.6 131.3 250 316 206.4 151.2 384 217 530.1 770.8 C D E F 106.8 65.52 94.4 102.1 153.7 215 G Hospital A B Patient-Days (65 or older) (1000s) 55.31 37.64 32.91 33.53 32.48 48.78 58.41 Output Measures Patient-Days (under 65) Nurses Interns ($1000s) Trained Trained 49.52 291 47 55.63 156 3 25.77 141 26 41.99 160 21 55.3 157 82 81.9 285 92 119.7 111 89 C D E F GStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


